Lucene
Apache LuceneTM is a high-performance, full-featured text search engine library written entirely in Java. It is a technology suitable for nearly any application that requires full-text search, especially cross-platform.
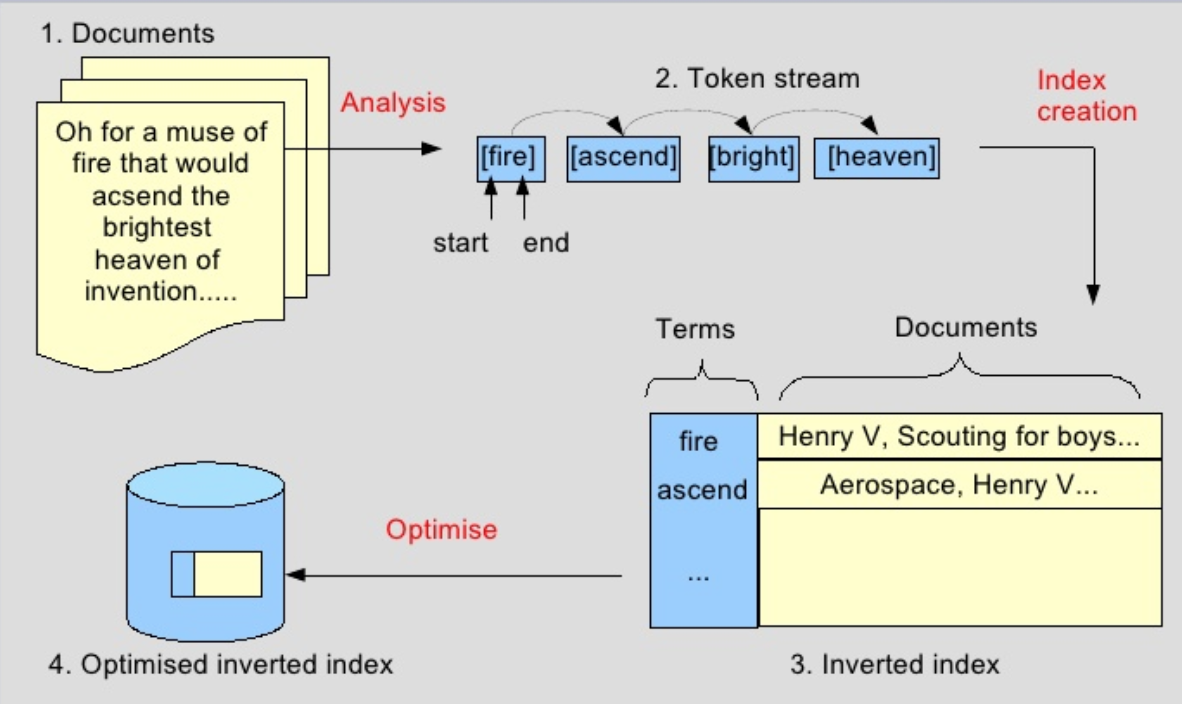
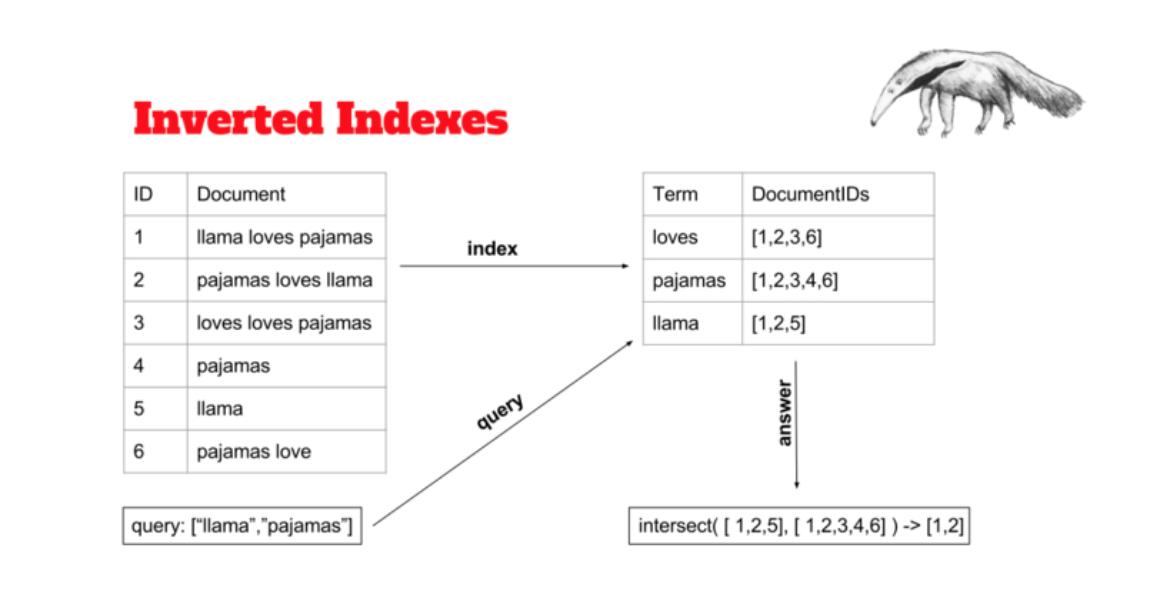
Reverse_index:
 (°0°)
(°0°)
 (°0°)
(°0°)
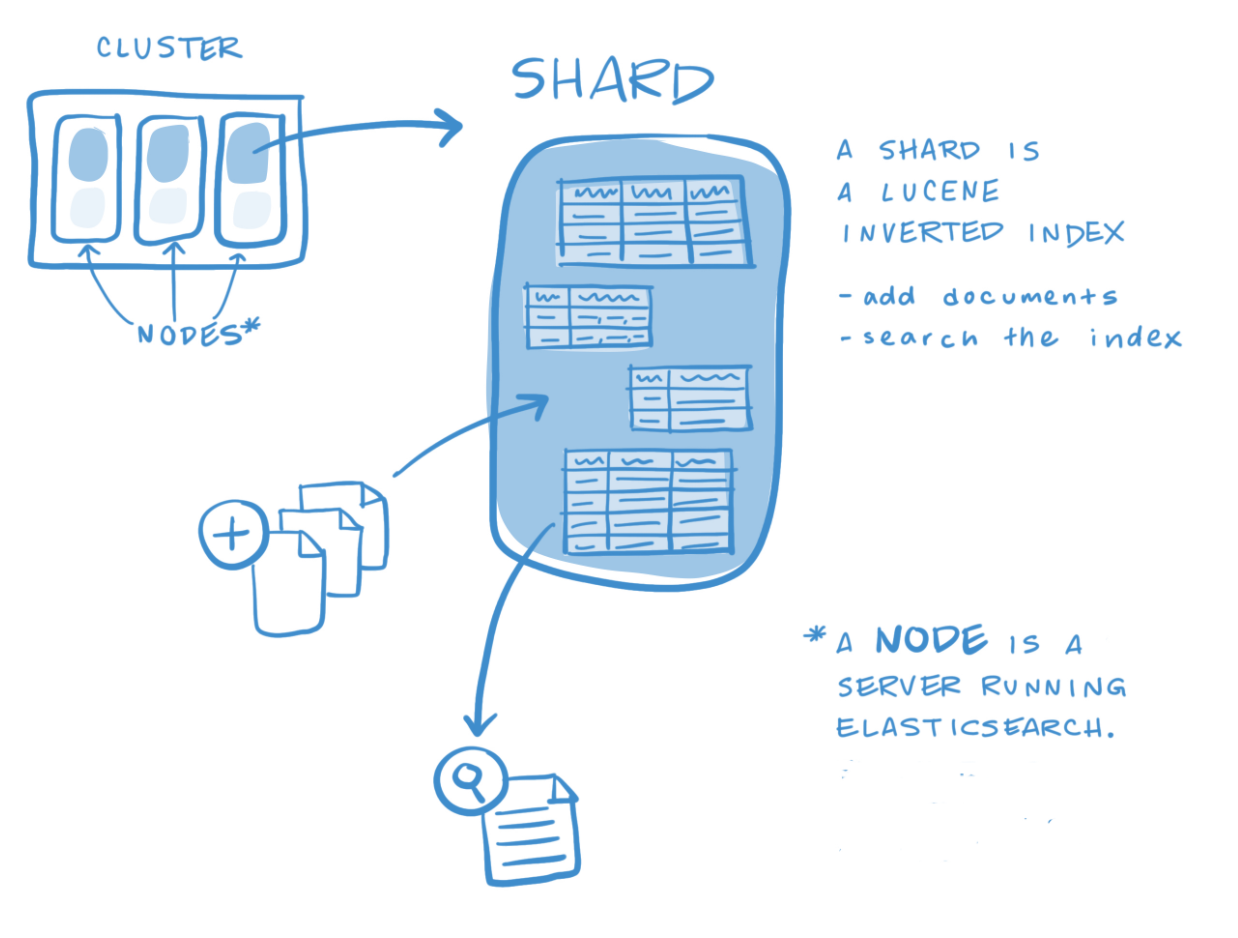
Elasticsearch Architecture
 (°0°)
(°0°)
 (°0°)
(°0°)
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Node type:
Master-eligible node
A node that has node.master set to true (default), which makes it eligible to be elected as the master node, which controls the cluster.
Data node
A node that has node.data set to true (default). Data nodes hold data and perform data related operations such as CRUD, search, and aggregations.
Ingest node
A node that has node.ingest set to true (default). Ingest nodes are able to apply an ingest pipeline to a document in order to transform and enrich the document before indexing. With a heavy ingest load, it makes sense to use dedicated ingest nodes and to mark the master and data nodes as node.ingest: false.
Tribe node
A tribe node, configured via the tribe.* settings, is a special type of coordinating only node that can connect to multiple clusters and perform search and other operations across all connected clusters.
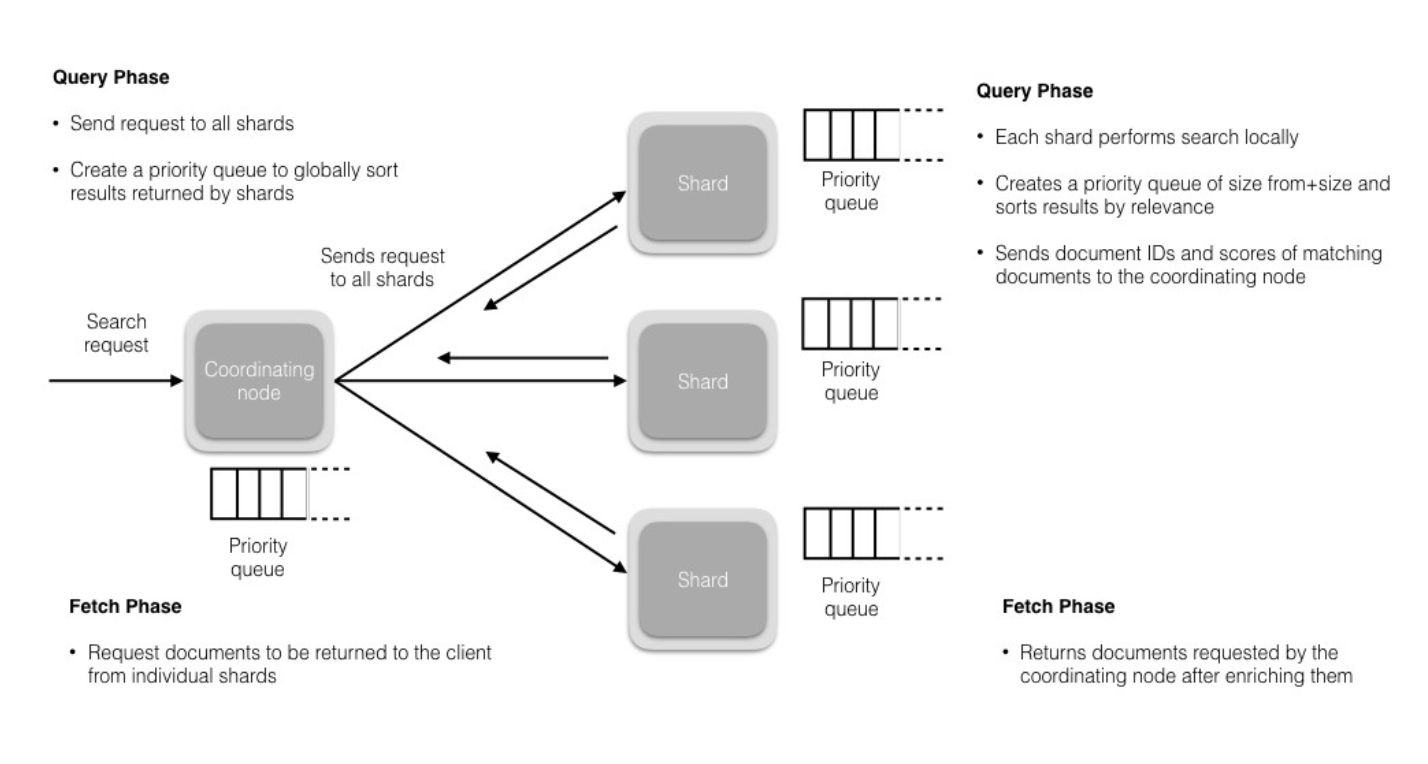
Coordinating node:
Every node is implicitly a coordinating node.A search request, for example, is executed in two phases which are coordinated by the node which receives the client request — the coordinating node.In the scatter phase, the coordinating node forwards the request to the data nodes which hold the data. Each data node executes the request locally and returns its results to the coordinating node. In the gather phase, the coordinating node reduces each data node’s results into a single global resultset.
Every node is implicitly a coordinating node. This means that a node that has all three node.master, node.data and node.ingest set to false will only act as a coordinating node, which cannot be disabled. As a result, such a node needs to have enough memory and CPU in order to deal with the gather phase.
Storage
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Index updated
-
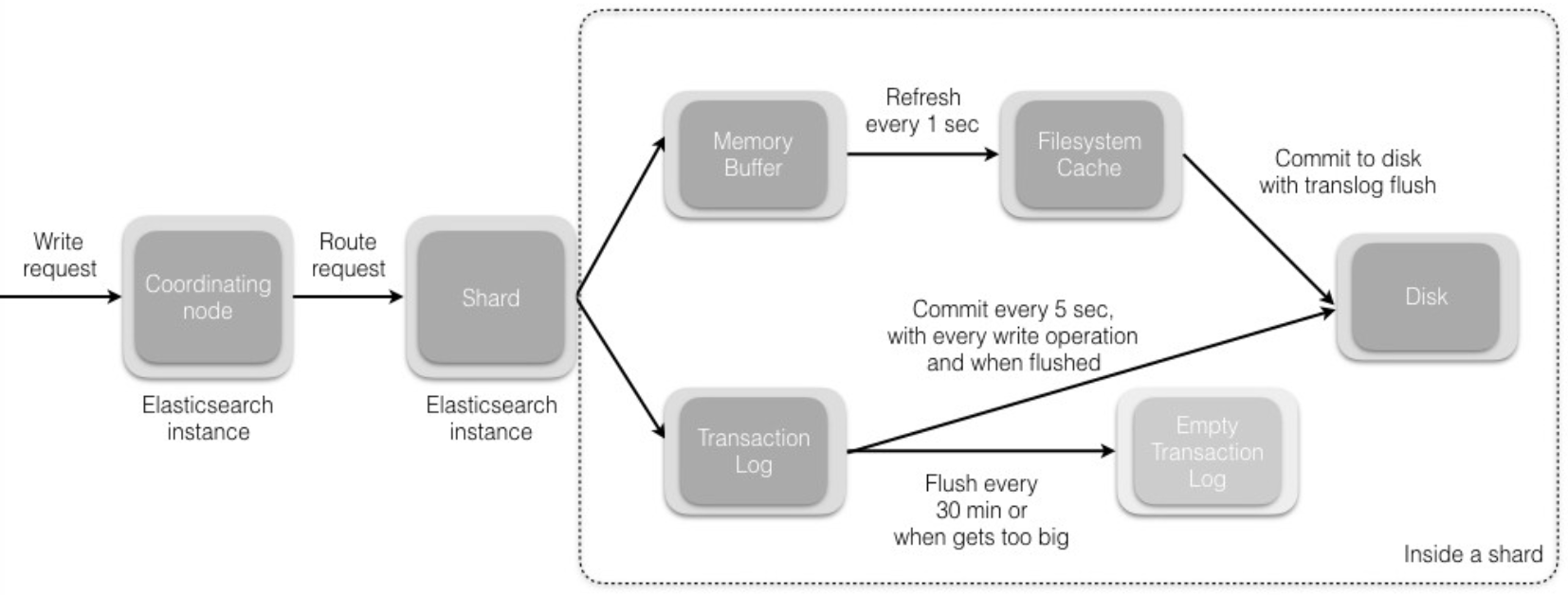
Index refresh
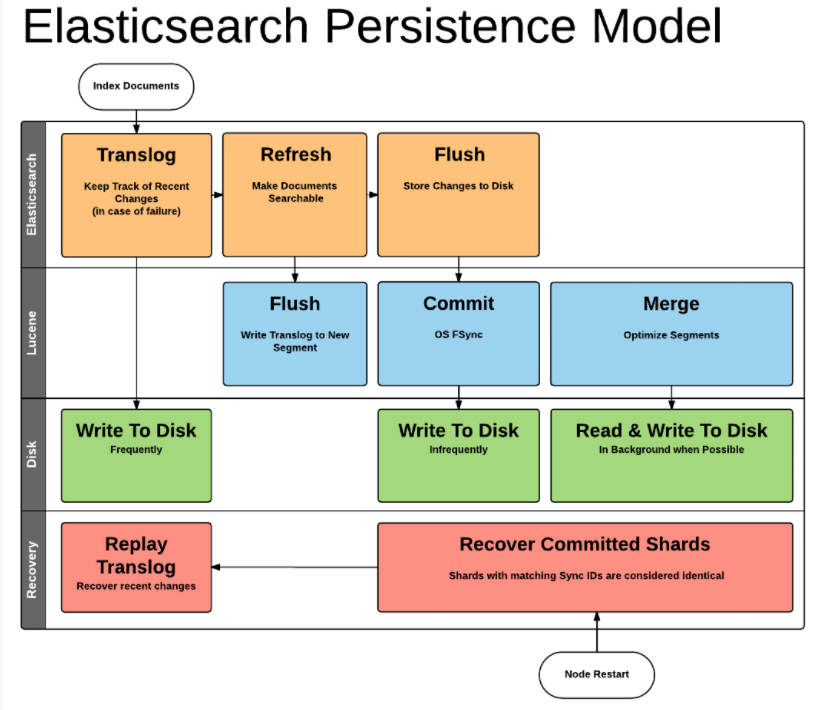
When new information is added to an index, or existing information is updated or deleted, each shard in the index is updated via two processes: refresh and flush.
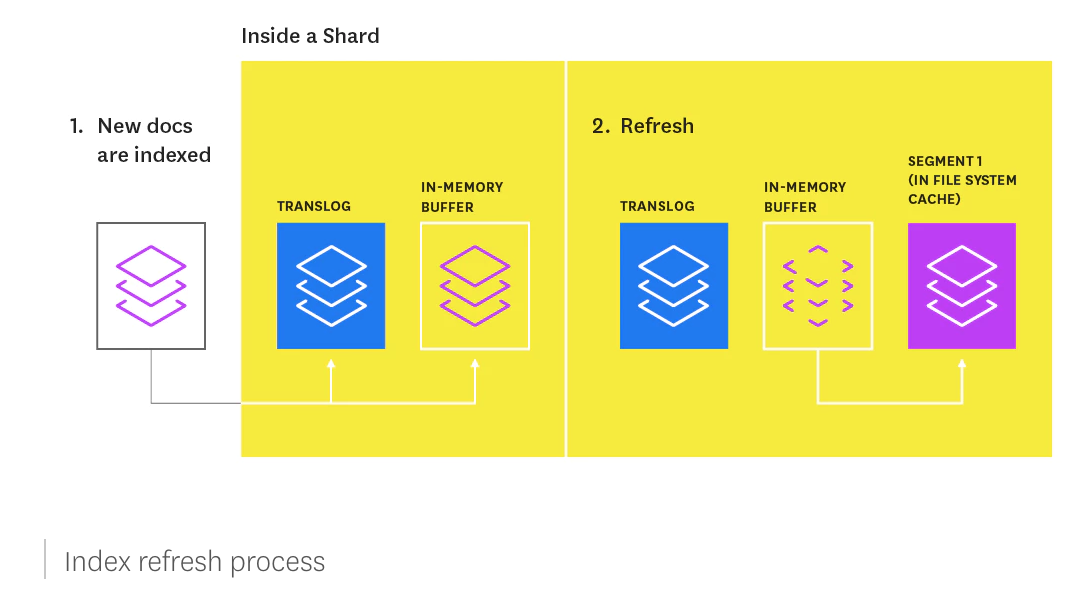
Newly indexed documents are not immediately made available for search. First they are written to an in-memory buffer where they await the next index refresh, which occurs once per second by default. The refresh process creates a new in-memory segment from the contents of the in-memory buffer (making the newly indexed documents searchable), then empties the buffer, as shown below.
A segment is immutable, so updating a document means:
writing the information to a new segment during the refresh process
marking the old information as deleted
The old information is eventually deleted when the outdated segment is merged with another segment.
 (°0°)
(°0°) -
Index flush
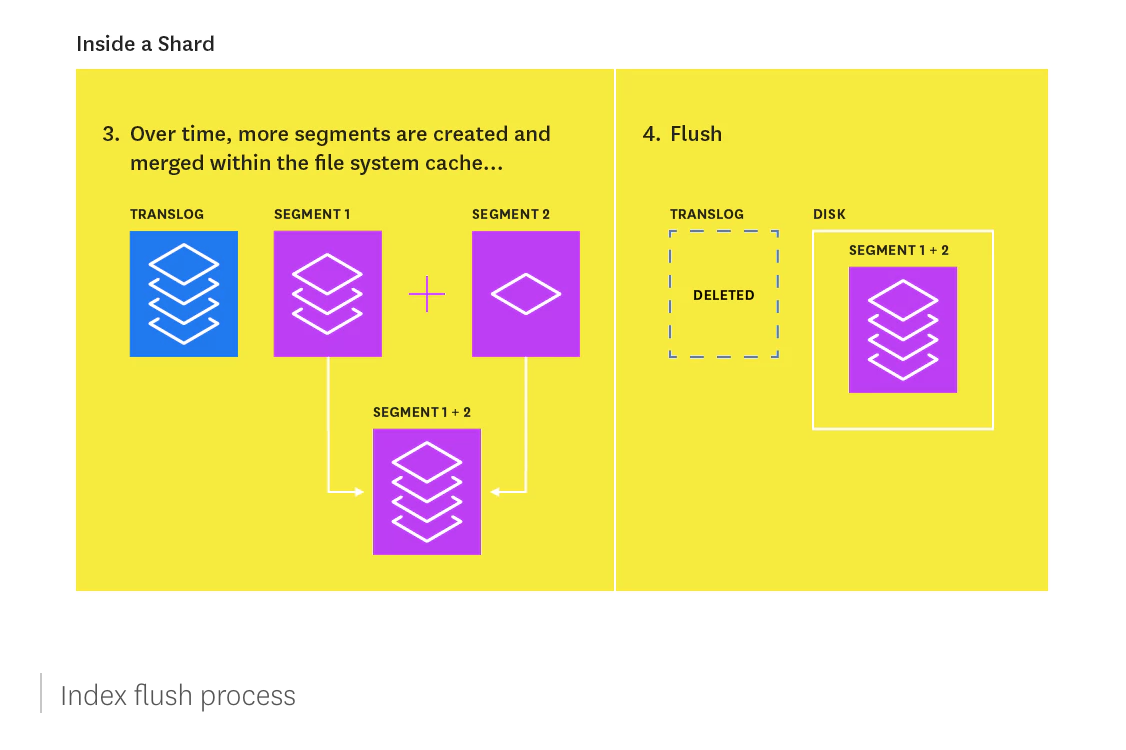
At the same time that newly indexed documents are added to the in-memory buffer, they are also appended to the shard’s translog: a persistent, write-ahead transaction log of operations. Every 30 minutes, or whenever the translog reaches a maximum size (by default, 512MB), a flush is triggered. During a flush, any documents in the in-memory buffer are refreshed (stored on new segments), all in-memory segments are committed to disk, and the translog is cleared.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Configuration
- Cluster:
node.master
node.data
cluster.name
discovery.zen.ping.multicast.enabled
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes - Shards:
index.number_of_shards
cluster.routing.allocation.same_shard.host - Replicas:
index.number_of_replicas - Durable:
gateway.type
index.refresh_interval - Transport:
transport.tcp.port
http.port - Recovery:
gateway.recover_after_nodes
gateway.recover_after_time
gateway.expected_nodes
cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries
indices.recovery.max_size_per_sec
indices.recovery.concurrent_streams - Memory:
bootstrap.mlockall - Path:
path.conf
path.data
path.work
path.logs
path.plugins - Memory:
bootstrap.mlockall - Network:
network.bind_host
network.publish_host
network.host
http.enabled
http.max_content_length
transport.tcp.compress - Cache
index.cache.field.type
index.cache.field.max_size
index.cache.field.expire - Translog
index.translog.flush_threshold_ops
index.translog.flush_threshold_size
index.translog.flush_threshold_period
index.translog.interval
index.gateway.local.sync - Merge
index.merge.policy.expunge_deletes_allowed
index.merge.policy.floor_segment
index.merge.policy.max_merge_at_once
index.merge.policy.max_merge_at_once_explicit
index.merge.policy.max_merged_segment
index.merge.policy.segments_per_tier
index.merge.policy.reclaim_deletes_weight - Other:
action.destructive_requires_name
Tuning
- Tips:
shard:
around 30G per shard.
refer
es:
datanode: node.master: false;node.data: true;http.enabled: false
masternode: node.master: true;node.data: false; http.enabled: true
bootstrap.mlockall: true
minimum_master_nodes:(based on quorum, node/2+1)
discovery.zen.ping.multicast.enabled: false
action.destructive_requires_name:true
action.auto_create_index: false
indices.fielddata.cache.size: 30%
indices.cache.filter.size: 30%
threadpool.bulk.queue_size: 5000
threadpool:
index:
type: fixed
size: 1000
search:
type: fixed
size: 3000
index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.warn: 5s
index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.info: 1s
index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.debug: 500ms
index.search.slowlog.threshold.query.trace: 200ms
index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.warn: 1s
index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.info: 800ms
index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.debug: 500ms
index.search.slowlog.threshold.fetch.trace: 200ms
index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.warn: 5s
index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.info: 2s
index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.debug: 1s
index.indexing.slowlog.threshold.index.trace: 100ms
script.engine.groovy.inline.aggs: true
script.engine.groovy.inline.search: true
index.cache.field.type: soft
index.cache.field.expire: 1m
index.cache.field.max_size: 5000
indices.cache.query.size: 2gb
indices.cache.filter.size: 2gb
indices.fielddata.cache.size: 2gb
#enable scripting to calculate distance
jvm:
the maximum JVM heap size recommendation for Elasticsearch is approximately 30-32GB.
-Xmx31g -Xms31g
ES_JAVA_OPTS=”-XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation -XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles=100 -XX:GCLogFileSize=10M -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode -XX:+CMSScavengeBeforeRemark -XX:+ParallelRefProcEnabled -XX:NewSize=5G -XX:MaxTenuringThreshold=15 -XX:SurvivorRatio=20 -XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=50 -XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
ES_GC_LOG_FILE=xx.gc.log
os:
vm.swappiness = 1
ulimit -n 65536
ulimit -l unlimited
ulimit -s unlimited
vm.max_map_count=655300
fs.file-max=518144
net.core.somaxconn=65535
hardware:
SSD raid0
RAM 96G
NIC 10Gb
Monitor
grafana
CommandsandTools
curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices
curl -XGET -u elastic:password http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
status:green/yellow(replicate has issue)/red(master has issue)
curl -XGET -u elastic:password http://localhost:9200/_nodes/stats?pretty=true
curl -XGET -u elastic:password http://localhost:9200/_cluster/pending_tasks?pretty
curl -XPOST ‘http://localhost:9200/_tasks/task_id:175591/_cancel’
curl -XGET -u elastic:password http://localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?help
curl -XPOST ‘http://localhost:9200/xx/_optimize’
curl -XGET localhost:9200/_cluster/state?pretty=true
curl -XGET -u elastic:password ‘http://localhost:9200/_cat/master’