Caching static assets
CDNs are the caching layer that is closest to the user.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Benefit
1, help reduce the load on our servers by removing the burden of serving static / bandwidth intensive resources
2, let us be present closer to our users
3, let us do geo-load balancing, in case we have multiple data centres around the world, and would want to serve from the closest data center (DC) possible.
4, improving website security by providing DDoS mitigation.
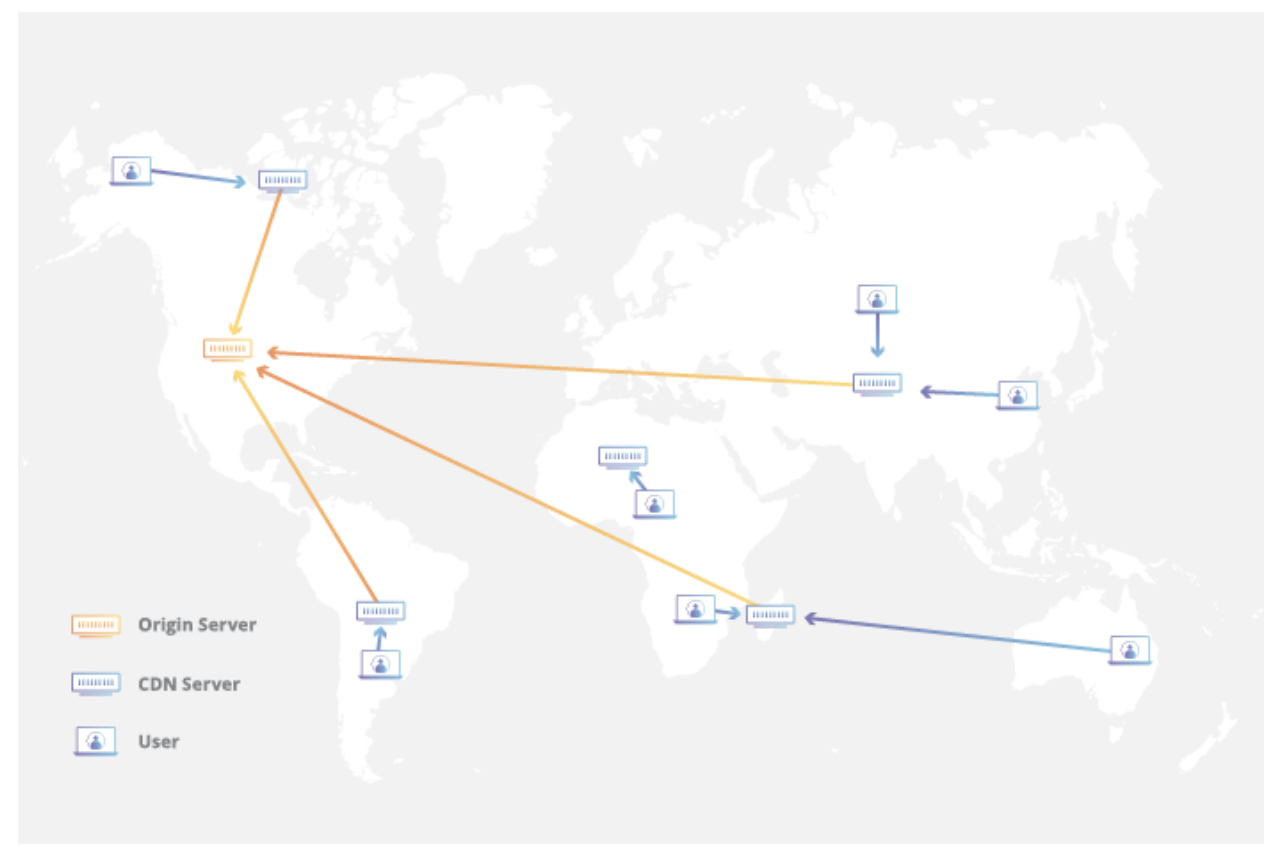
Points of Presence(POP)
CDN POPs are geographically distributed data centers aimed at being close to users.
POPs typically may not have all the content, but have caching servers that cache the static assets, and fetch the rest of the content from the origin server where the application actually resides.
Sticky Routing
It might be simply pinning all users to a specific DC or pinning specific users to specific servers. This is typically done from the POP, so that as soon as the user enters reaches our servers, we can route them to the nearest DC possible.
Geo DNS
When a user opens the application, the user can be directed to one of the multiple globally distributed POPs. This can be done using GeoDNS, which simply put, gives out a different IP address(which are distributed geographically), depending on the location of the user making the DNS request.
Reliability and Redundancy
A well-rounded CDN has several features that will minimize downtime:
Load balancing distributes network traffic evenly across several servers, making it easier to scale rapid boosts in traffic.
Intelligent failover provides uninterrupted service even if one or more of the CDN servers go offline due to hardware malfunction; the failover can redistribute the traffic to the other operational servers.
In the event that an entire data center is having technical issues, Anycast routing transfers the traffic to another available data center, ensuring that no users lose access to the website.
LinkedIn example
trafficshift