route53
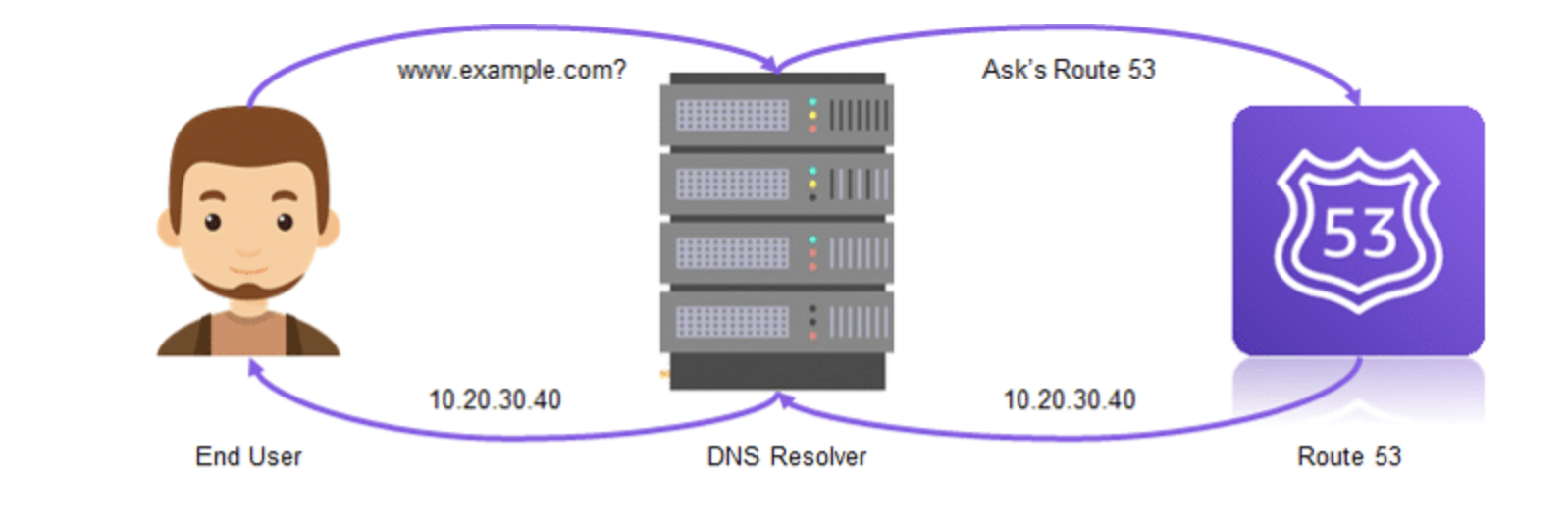
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
- AWS Route 53 connects requests to the infrastructure running in AWS. These requests include elastic load balancing, Amazon EC2 instances, or Amazon S3 buckets.
- In addition to this, AWS Route 53 is also used to route users to infrastructure outside of AWS.
Benefits
- DNS servers are distributed across many availability zones, which helps in routing end users to your website consistently.
- Fast, they route users to the nearest DNS server available.
Limitations
No DNSSEC support: DNSSEC stands for Domain Name System Security Extensions. It is a suite of extensions specifications by the Internet Engineering Task Force. It is used to secure the data exchanged in DNS in Internet Protocol networks. It is not supported by AWS Route 53.
Forwarding options: Route 53 does not provide forwarding or conditional forwarding options for domains used on an on-premise network.
Single point of failure: Used in conjunction with other AWS services, Route 53 may become a single point of failure. This becomes a major problem for AWS route 53 disaster recovery and other relevant issues.
Limited Route 53 DNS load balancing: The features of AWS Route 53 load balancer lack advanced policy support and enterprise-class features and provide only basic load balancing capabilities.
Route 53 Cost: For businesses using Route 53 with non-AWS endpoints or services, the service is expensive. In particular, the visual editor is costly including the cost of each query.
No support for private zone transfers: AWS Route 53 DNS cannot be appointed as the authoritative source for cloud websites.com, even after having the root-level domain registered.
Latency: All AWS Route 53
Features
Traffic Flow
You can route end users to the best endpoint possible according to your application’s geo proximity, latency, health, and other considerations.
Latency-based Routing
You can route end users to the AWS region with the lowest possible latency.
Geo DNS
You can route your end users to the endpoint which is present in their specific region or the nearest geographic location.
DNS Failover
You can route your end users to an alternate location to avoid website crashes or outages