service mesh
- what is service mesh
A service mesh is a software infrastructure layer for controlling communication between services; it’s generally made of two components:The data plane, which handles communications near the application. Typically this is deployed with the application as a set of network proxies, as illustrated earlier. The control plane, which is the “brain” of the service mesh. The control plane interacts with proxies to push configurations, ensure service discovery, and centralize observability. - goals
Connectivity : communication resiliency, such as retries, timeouts, circuit breaking, and rate limiting, routing control in the form of traffic shifting and mirroring
Security: encrypting internal traffic adds a welcome layer of extra complexity in case of a system breach. all service meshes use mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption for interservice communication
Observability: a service mesh enforces observability, providing layer-seven metrics, which in turn allow for automatic alerts when traffic reaches some customizable threshold.
envoy
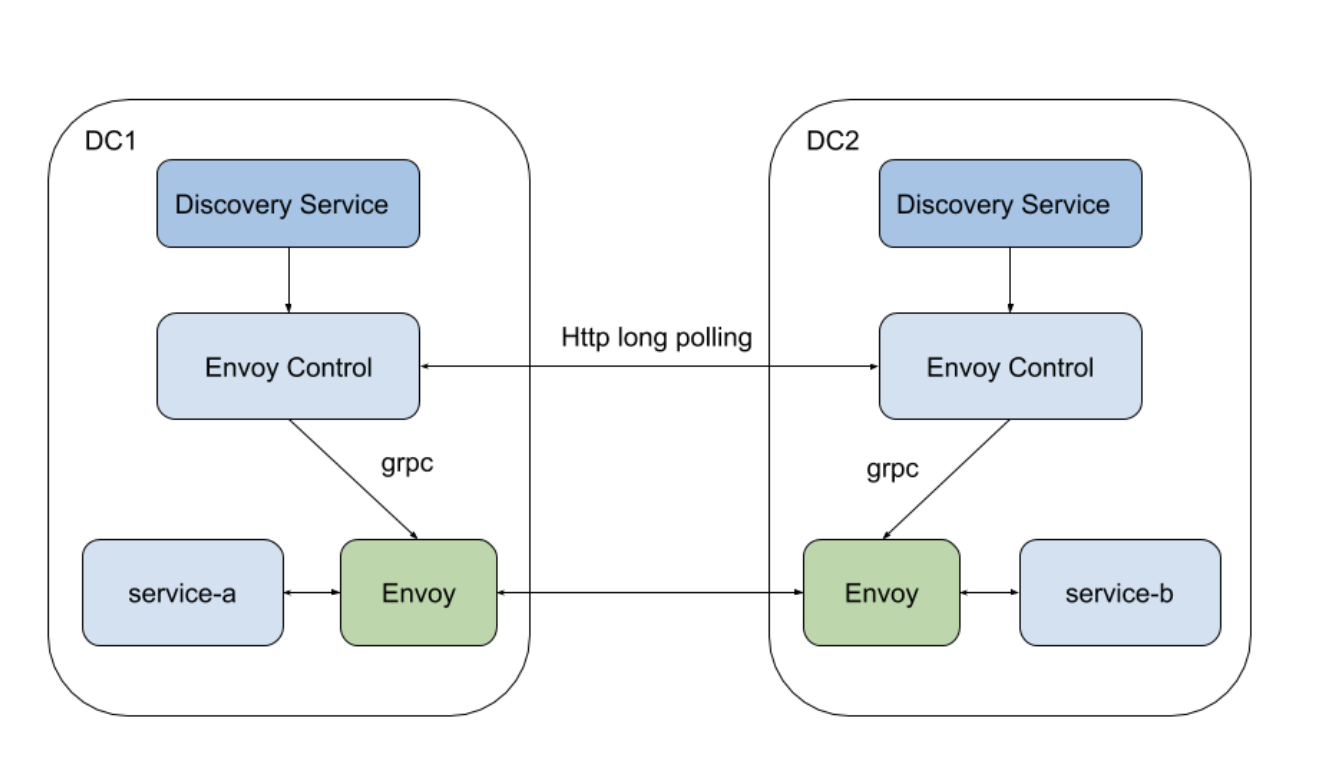 (°0°)
(°0°)
Envoy was designed from the ground up for microservices, with features such as hitless reloads (called hot restart), observability, resilience, and advanced load balancing.
-
lifecycle
(°0°)
-
components:
Listener Discovery Service (LDS)
Route Discovery Service (RDS)
Endpoint Discovery Service (EDS) - through kube-apiserver by Kubernetes Informer, Informers query the resource data and store it in a local cache. Once stored, an event is only generated when it detects a change in the object (or resource) state.
Secret Discovery Service (SDS)
- pros
Envoy, while supporting a static configuration model, also allows configuration via gRPC/protobuf APIs. This simplifies management at scale, and also allows Envoy to work better in environments with ephemeral services.