What is Spinnaker
Spinnaker is an open source, multi-cloud continuous delivery platform for releasing software changes with high velocity and confidence.
- multi-cloud
Deploy across multiple cloud providers including AWS EC2, Kubernetes, Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, Openstack, Cloud Foundry, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, with DC/OS coming soon. - Automated Releases
Create deployment pipelines that run integration and system tests, spin up and down server groups, and monitor your rollouts. Trigger pipelines via git events, Jenkins, Travis CI, Docker, CRON, or other Spinnaker pipelines. - Built-in Deployment Best Practices
Create and deploy immutable images for faster rollouts, easier rollbacks, and the elimination of hard to debug configuration drift issues. Leverage an immutable infrastructure in the cloud with built-in deployment strategies such as red/black and canary deployments.
Concepts
 (°0°)
(°0°)
- application management
Applications:
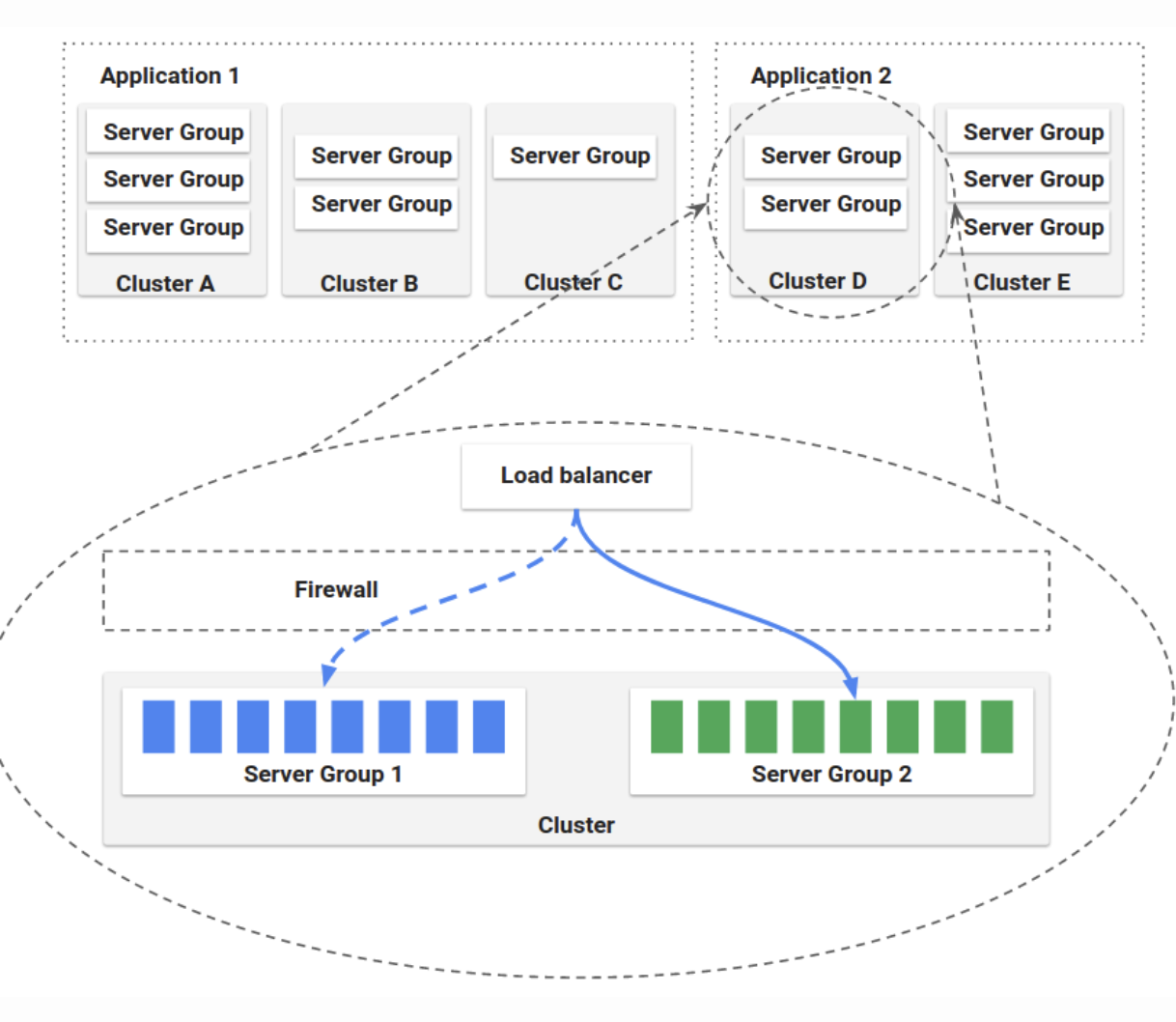
An application in Spinnaker is a collection of clusters, which in turn are collections of server groups. The application also includes firewalls and load balancers.
An application represents the service which you are going to deploy using Spinnaker, all configuration for that service, and all the infrastructure on which it will run.
cluster:
You can define Clusters, which are logical groupings of Server Groups in Spinnaker.
Note: cluster, here, does not map to a Kubernetes cluster. It’s merely a collection of Server Groups, irrespective of any Kubernetes clusters that might be included in your underlying architecture.
server group:
The base resource, the Server Group, identifies the deployable artifact (VM image, Docker image, source location) and basic configuration settings such as number of instances, autoscaling policies, metadata, etc. This resource is optionally associated with a Load Balancer and a Firewall. When deployed, a Server Group is a collection of instances of the running software (VM instances, Kubernetes pods).
-
application deployment
pipeline
 (°0°)
(°0°)
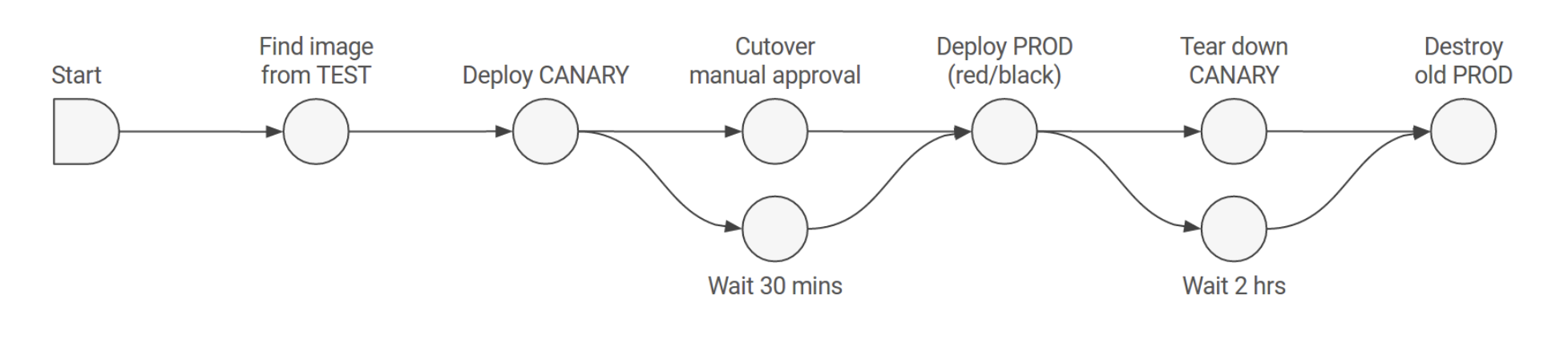
The pipeline is the key deployment management construct in Spinnaker. It consists of a sequence of actions, known as stages. You can pass parameters from stage to stage along the pipeline.
A Stage in Spinnaker is an atomic building block for a pipeline, describing an action that the pipeline will perform, like Deploy, Resize, Disable, Manual Judgment(Evaluate) -
Deployment strategies
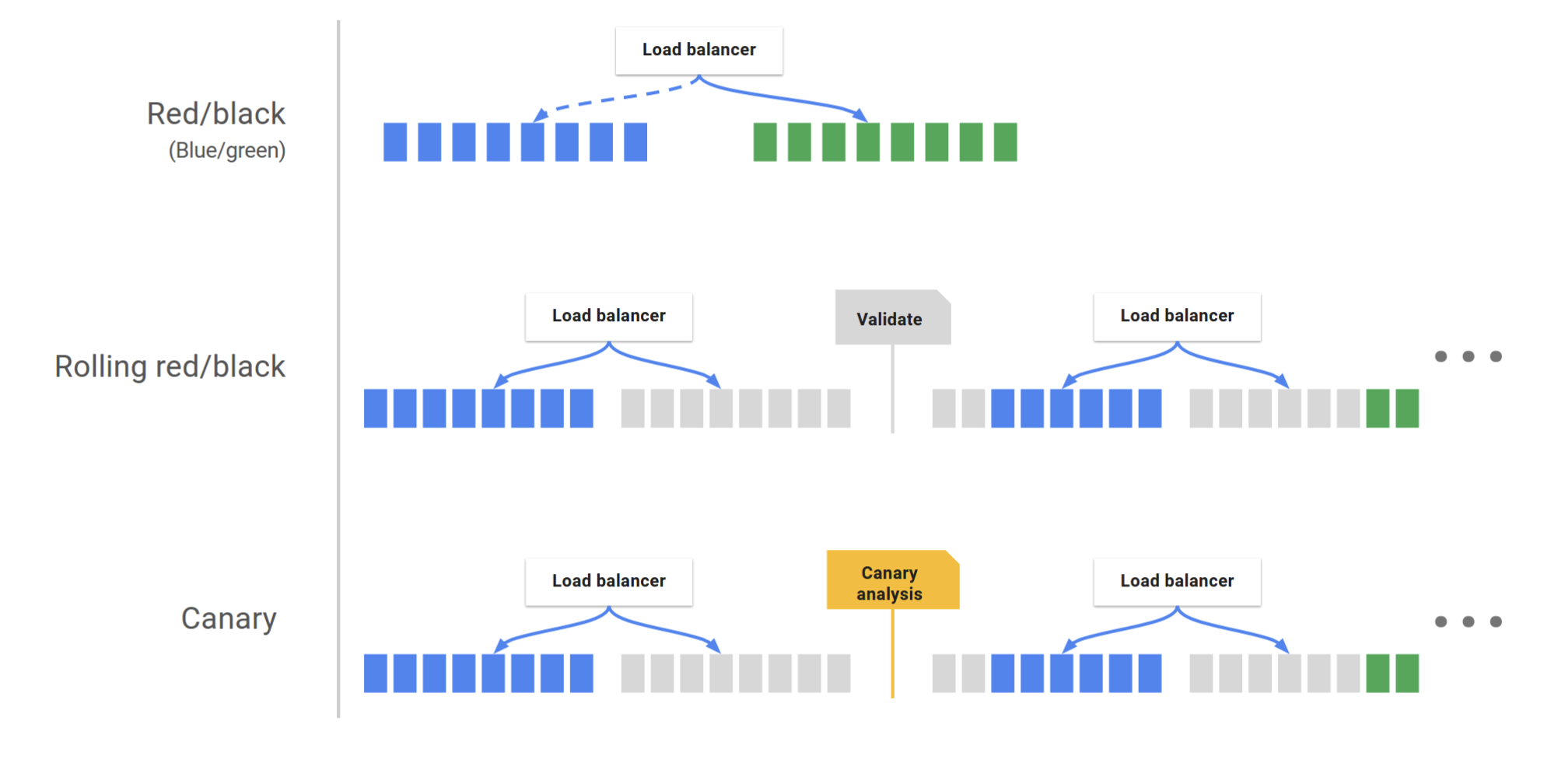
Spinnaker supports the red/black (a.k.a. blue/green) strategy, with rolling red/black and canary strategies in active development.
Canary is a deployment process in which a change is partially rolled out, then evaluated against the current deployment (baseline) to ensure that the new deployment is operating at least as well as the old. This evaluation is done using key metrics that are chosen when the canary is configured.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
blue/green can avoid the issues when one deployment with newer version but another deployment with current/old version when release deployment is going on -
workflow(in pipeline)
git repo changes -> jenkins build job -> spinnaker(trigger) –> spinnaker CI(call jenkins job) –> spinnaker CD – > aws(infra) –> eks(services) –> jenkins(post-check)
1, git repo changes
2, jenkins build job triggered by step 1
3, spinnaker is triggered by jenkins build and start app CI stage
4, spinnaker start CD stage when CI stage finish successfully
5, spinnaker trigger jenkins to post-check
-
pipeline template
Pipeline Templates help you standardize and distribute reusable Pipelines across your team or among multiple teams. Like “app” is variable with other static env configs. -
spin command
$ cat ~/.spin/config gate: endpoint: https://gate.spinnaker.domain auth: enabled: true basic: username: LDAP_USERNAME password: LDAP_PASSWORD
microservices
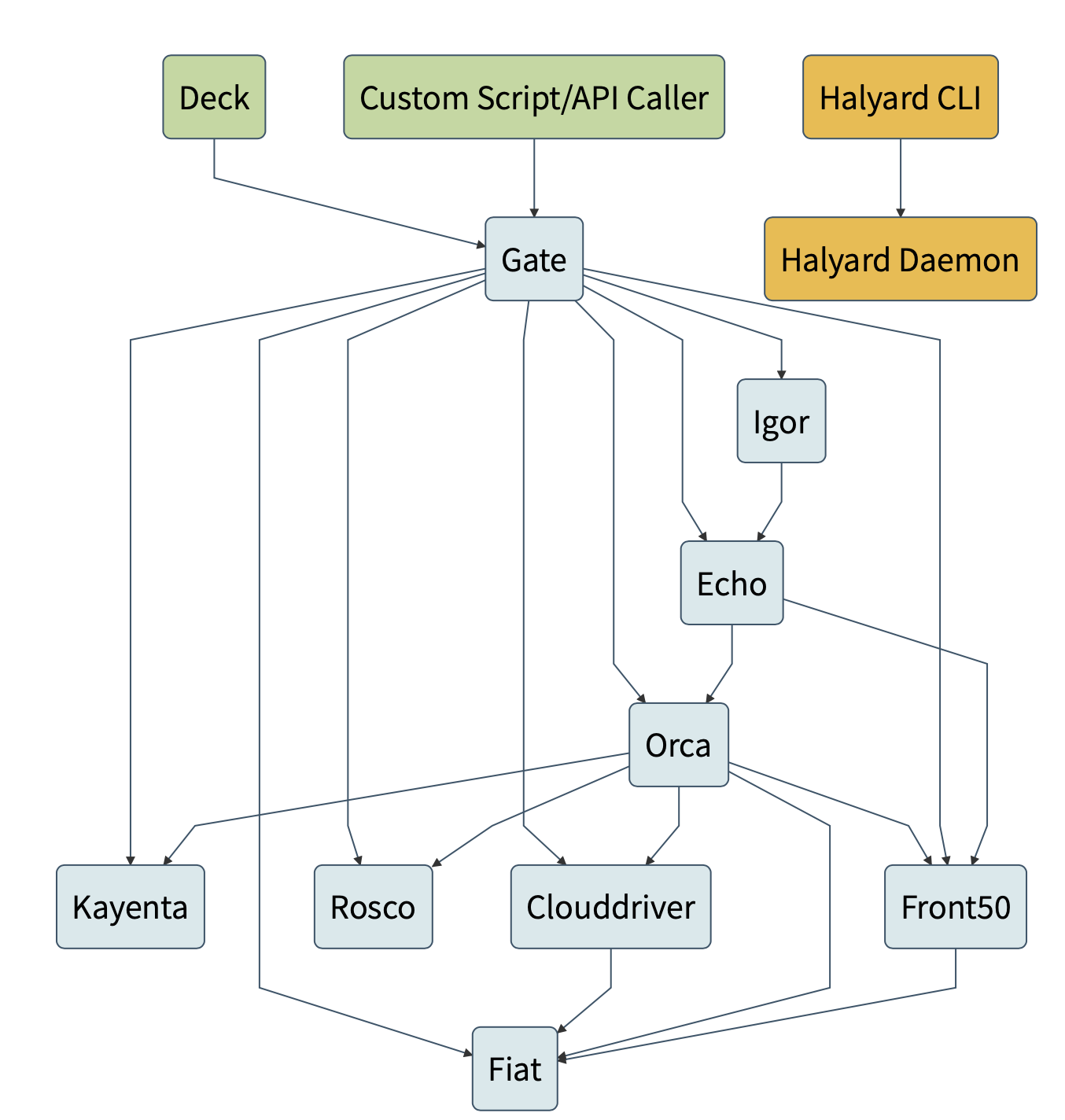
Spinnaker is composed of a number of independent microservices:
- Deck is the browser-based UI.
- Gate is the API gateway. The Spinnaker UI and all api callers communicate with Spinnaker via Gate.
- Orca is the orchestration engine. It handles all ad-hoc operations and pipelines. Read more on the Orca Service Overview.
- Clouddriver is responsible for all mutating calls to the cloud providers and for indexing/caching all deployed resources.
- Front50 is used to persist the metadata of applications, pipelines, projects and notifications.
- Rosco is the bakery. It produces immutable VM images (or image templates) for various cloud providers. It is used to produce machine images (for example GCE images, AWS AMIs, Azure VM images). It currently wraps packer, but will be expanded to support additional mechanisms for producing images.
- Igor is used to trigger pipelines via continuous integration jobs in systems like Jenkins and Travis CI, and it allows Jenkins/Travis stages to be used in pipelines.
- Echo is Spinnaker’s eventing bus. It supports sending notifications (e.g. Slack, email, SMS), and acts on incoming webhooks from services like Github.
- Fiat is Spinnaker’s authorization service.It is used to query a user’s access permissions for accounts, applications and service accounts.
- Kayenta provides automated canary analysis for Spinnaker.
- Halyard is Spinnaker’s configuration service.Halyard manages the lifecycle of each of the above services. It only interacts with these services during Spinnaker startup, updates, and rollbacks.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Kayenta
- Automated Canary Analysis
- features
- Metric Retrieval
- Jugement(Data validation, Data cleaning, Metric Comparison, Score Computation)
- Reporting
refer
- deployment by Halyard, enable canary
refer
lifecycle
- deployment
(°0°)
- bake
(°0°)
stageEnabled
application: xxx
name: xxx
pipeline: idxxx
stageEnabled: {
expression: parameters.cluster matches ‘a1|a2|a3|a4’
type: expression
}