kube-proxy
As a reverse proxy, kube-proxy is responsible for watching client requests to some IP:port and forwarding/proxying them to the corresponding service/application on the private network. However, the difference between the kube-proxy and a normal reverse proxy is that the kube-proxy proxies requests to Kubernetes Services and their backend Pods, not hosts.
kube-proxy modes
Kube-proxy can work in three different modes:
-
userspace
In the userspace mode, most networking tasks, including setting packet rules and load balancing, are directly performed by the kube-proxy operating in the userspace. In this mode, kube-proxy comes the closest to the role of a reverse proxy that involves listening to traffic, routing traffic, and load balancing between traffic destinations. Also, in the userspace mode, kube-proxy must frequently switch context between userspace and kernelspace when it interacts with iptables and does load balancing. -
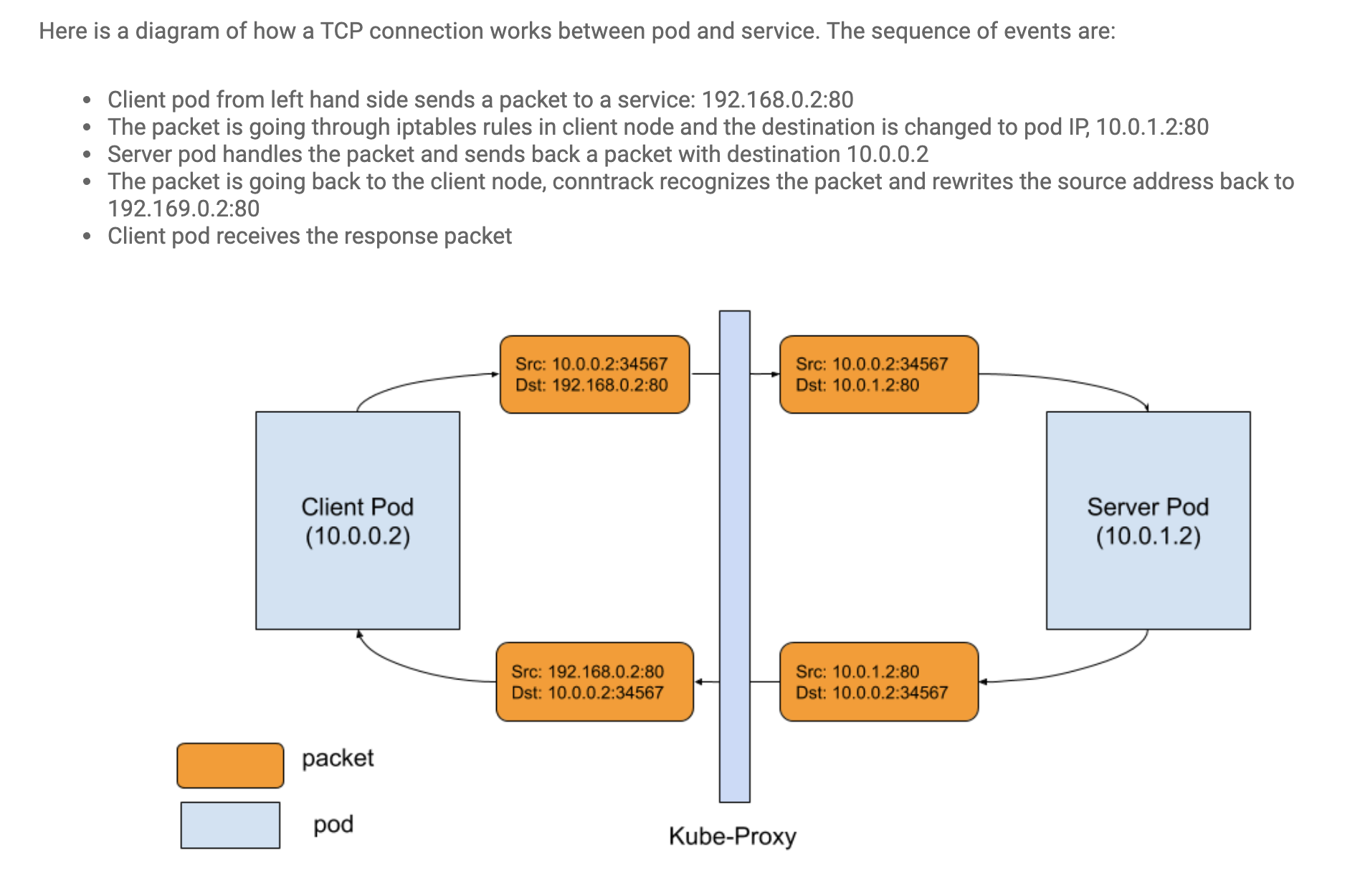
iptables(kernel namespace)
In the iptables mode, kube-proxy no longer works as a reverse proxy load balancing the traffic between backend Pods. This task is delegated to iptables/netfilter. Iptables is tightly integrated with netfilter, so there is no need to frequently switch context between the userspace and the kernelspace. -
IPVS(hashtable is better than iptables)
In the IPVS mode, load balancing is performed using IPVS (IP Virtual Server). Built on top of netfilter, IPVS (IP Virtual Server) implements transport-layer load balancing as part of the Linux kernel.
IPVS was specifically designed for load balancing, and it uses hash tables to store network rules more efficiently than iptables. This allows for almost unlimited scale and fast network throughput as all processes occur in the kernelspace.
kube-proxy watches K8s Services and Pod Endpoints. If a new Service is created, kube-proxy calls the netlink interface to create IPVS rules.
Also, it periodically syncs IPVS rules with the K8s Services and Endpoints to make sure that the desired state is maintained.
When Service is accessed, IPVS load balancer redirects traffic to backend Pods.
debug conn
 *(°0°)
*(°0°)
connection