 (°0°)
(°0°)
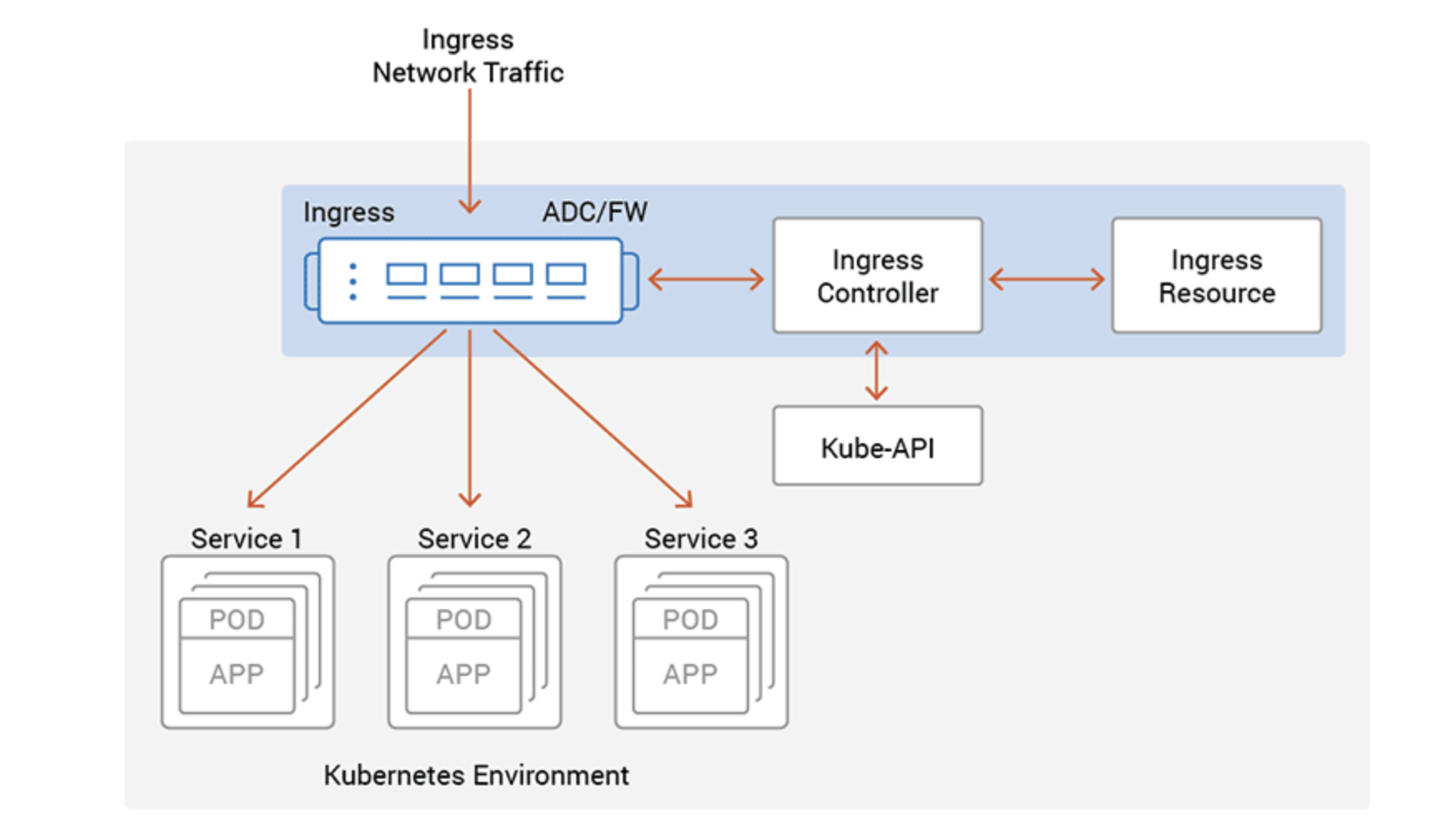
Ingress
Ingress is an API object that manages external access to services in the
cluster, mostly over HTTP/HTTPS , like a collection of routing rules that gaven how external users access services running in a Kubernetes cluster.
Ingress Resources
The ingress resource contains metadata configuration parameters for the third-party systems. These parameters include security policies, routing rules and traffic steering parameters. The ingress controller works with the ingress resource to automatically provision application delivery systems.
- example:
```
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hello-world
spec:
rules:- http:
paths:- path: /api/hello-world
backend:
serviceName: hello-world
servicePort: 80
```
- path: /api/hello-world
- http:
Ingress Controllers
The ingress controller is a Kubernetes service responsible for managing ingress network traffic. This is primarily accomplished by providing an interface between the Kubernetes environment and third-party ingress systems like network and security systems. These systems have proprietary management interfaces, so the ingress controller is also provided by the third-party vendor.
Monitor Ingress resources via the Kubernetes API and update the configuration of a load balancer in case of any changes.Acts as reverse proxy for the Ingress rules found at api-server’s /ingresses endpoint
There are multiple ways to access an Ingress Controller from outside of a cluster:
HostPorts - You can configure each pod to accept traffic on a host port
NodePorts - You can create a node port service to forward traffic to the IC from the service port on every node LoadBalancer - Cloud deployments can use LB services for forward traffic to the IC.
client --> Ingress Controller(deployment, should be on multiple nodes with same ip and port, usually keepalived) --> ingress(rules)
--> service --> deployment(pod)
multi controllers
ingress-class + annotations
Methods to route traffic
refer
- proxy + clusterIP
- NodePort
- Ingress
- Load Balncer
metallb
refer
MetalLB is a Loadbalancer implementation for bare metal Kubernetes clusters, based on standard routing protocols.
For this a network address pool must be reserved for MetalLB. Once MetalLB has assigned an external IP address to a service, it needs to redirect the traffic from the external IP to the cluster. To do so, MetalLB uses standard protocols such as ARP, NDP, or BGP.
- configMap
Each service will pick one IP from ConfigMap’s data.config.address-pools.addresses. The IP here should be external ip and not used by any other host. Usually this IP would point to ingress controller
So every TOR should send request to hosts(which are peered) and the kube-proxy on these hosts can resolve this vip to specific service.
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
peers:- peer-address: 10.0.0.1
peer-asn: 64501
my-asn: 64500
address-pools: - name: default
protocol: bgp
addresses:- 192.168.10.0/24
```
refer bgp
- 192.168.10.0/24
- peer-address: 10.0.0.1
- controller
Deployment, get config from configMap, this component is responsible for receiving allocation requests. -
speaker
DaemonSet, get config from configMap, the speaker must be installed on each node in the cluster to advertise ip address -
traffic flow(metallb)
IP address –> TOR switches –> peer hosts(nodes) –> kube-proxy(find k8s service by IP and then find pods by selector) - example
```
kubectl get svc -n ingress-services
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-services traefik-ingress-service LoadBalancer C-IP E-IP 443:31206/TCP,80:31862/TCP,8080:30910/TCP 1d
kubectl describe service traefik-ingress-service -n ingress-services
Name: traefik-ingress-service
Namespace: ingress-services
Labels:
kubectl get pods -l app=traefik –all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-services traefik-controller-998b6666-c6666 1/1 Running 0 1d
```