api
The API Server is the main management point of the entire cluster. In short, it processes REST operations, validates them, and updates the corresponding objects in etcd.
The API Server is the only Kubernetes component that connects to etcd; all the other components must go through the API Server to work with the cluster state.
all activei
scheduler
leader
A scheduler watches for newly created Pods that have no Node assigned. For every Pod that the scheduler discovers, the scheduler becomes responsible for finding the best Node for that Pod to run on.
In a cluster, Nodes that meet the scheduling requirements for a Pod are called feasible nodes. If none of the nodes are suitable, the pod remains unscheduled until the scheduler is able to place it.
kube-scheduler selects a node for the pod in a 2-step operation:
1,Filtering
2,Scoring
controller
leader
In Kubernetes, a controller is a control loop that watches the shared state of the cluster through the apiserver and makes changes attempting to move the current state towards the desired state. Examples of controllers that ship with Kubernetes today are the replication controller, endpoints controller, namespace controller, and serviceaccounts controller.
Besides, the Controller Manager performs lifecycle functions such as namespace creation and lifecycle, event garbage collection, terminated-pod garbage collection, cascading-deletion garbage collection, node garbage collection, etc.
workflow
 (°0°)
(°0°)
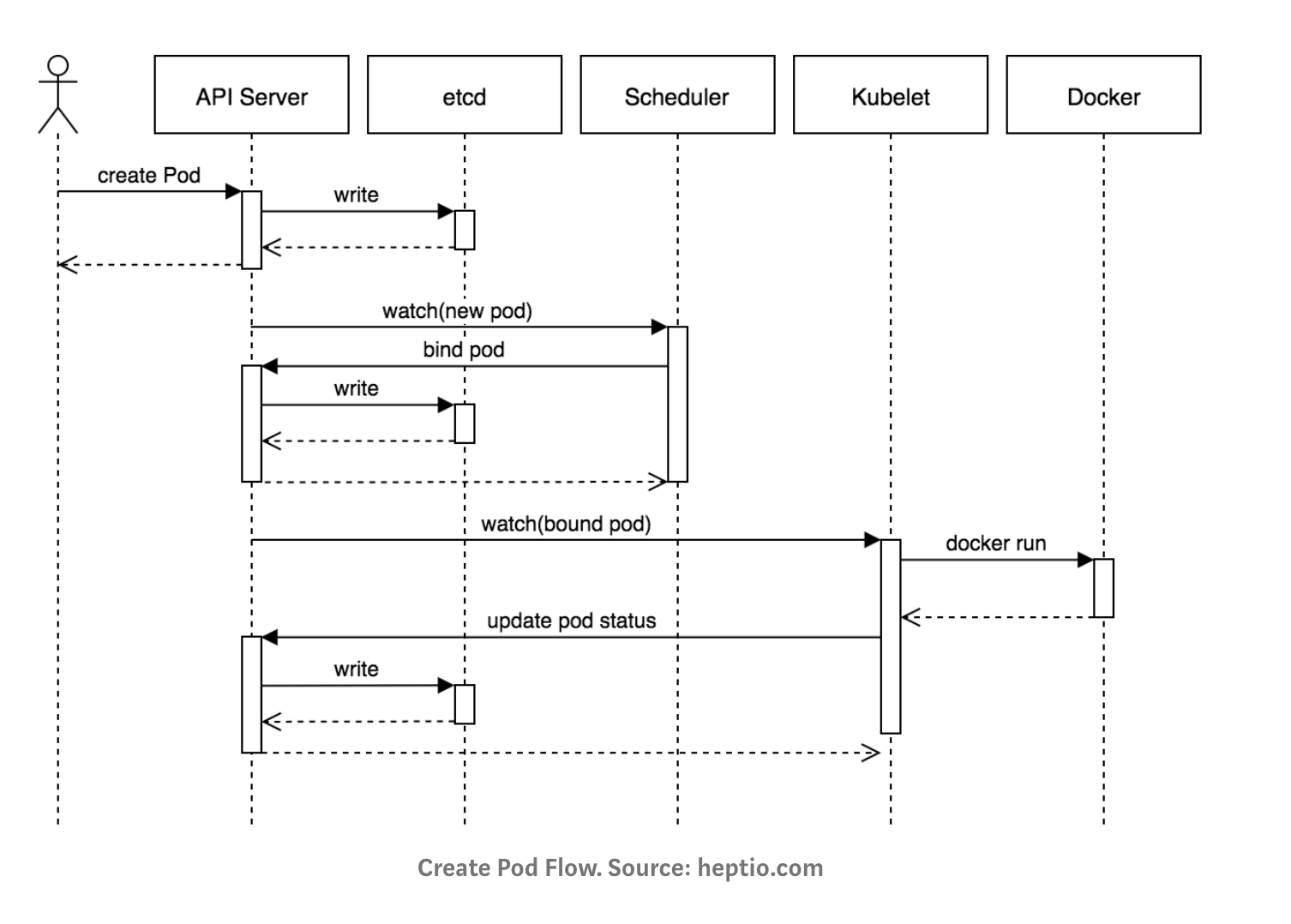
- create a pod
1.kubectl writes to the API Server.
2.API Server validates the request and persists it to etcd.
3.etcd notifies back the API Server.
4.API Server invokes the Scheduler.
5.Scheduler decides where to run the pod on and return that to the API Server.
6.API Server persists it to etcd.
7.etcd notifies back the API Server.
8.API Server invokes the Kubelet in the corresponding node.
9.Kubelet talks to the Docker daemon using the API over the Docker socket to create the container.
10.Kubelet updates the pod status to the API Server.
11.API Server persists the new state in etcd.
custom controllers
refer
faster reschedule
–node-status-update-frequency from 10s to 4s
–node-monitor-period from 5s to 2s
–node-monitor-grace-period from 40s to 20s
–pod-eviction-timeout from 5m to 30s