Stages of linux boot process
-
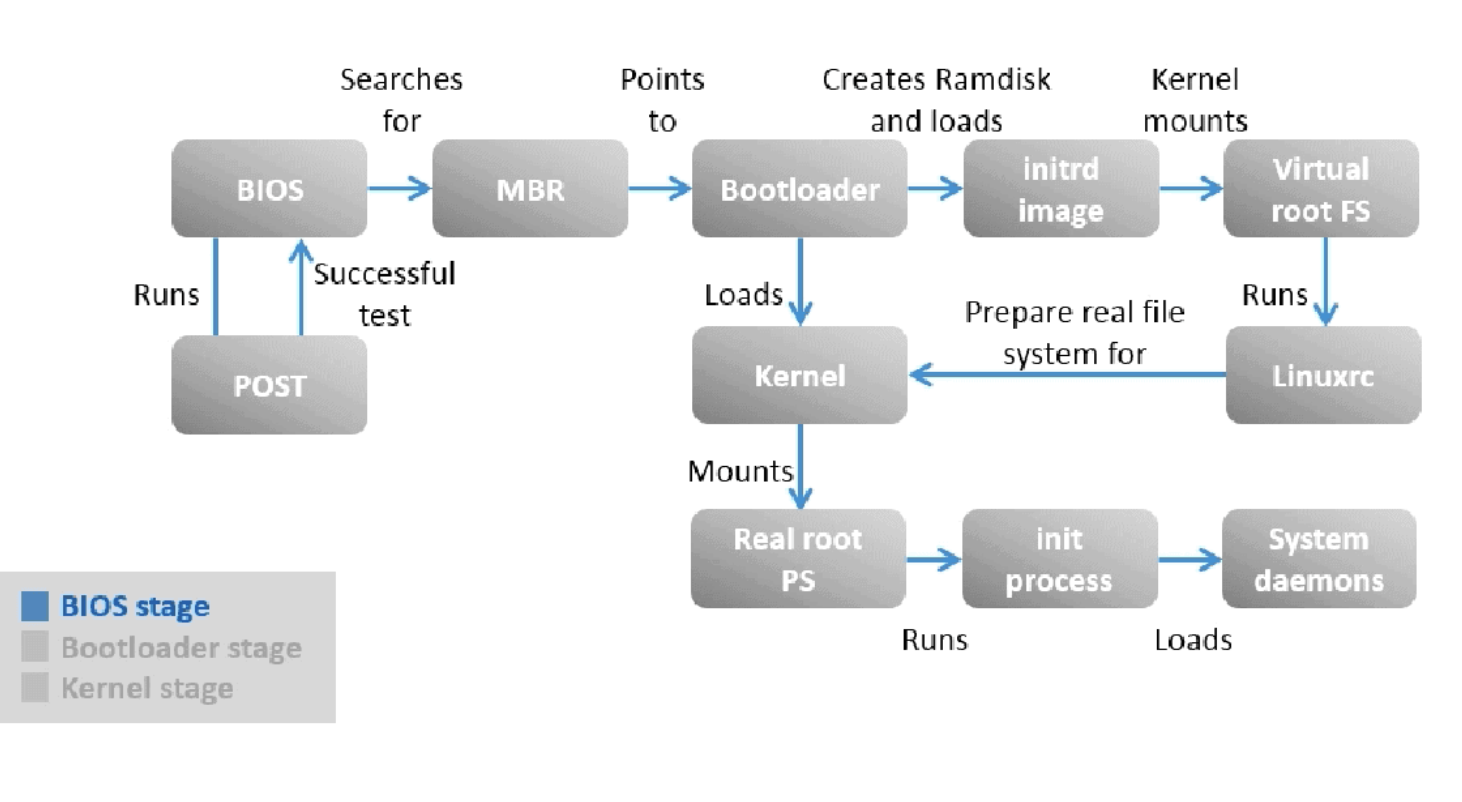
BIOS stage
When the machine is powered on BIOS is the first one to be called to verify if the hardware is present in the machine and if it is functioning.
This is done by performing a Power On Self Test (POST)
After a successful test, BIOS checks the MBR (Master Boot Record) in the hard disk to check if it refers to the location of the boot loader.
The MBR is a 512-byte code that is located on the first sector of the hard drive which is usually /dev/sda or /dev/hda depending on your hard drive architecture. -
Boot Loader Stage
The boot loader will be installed if an operating system is installed on the system.GRUB2 stands for GRand Unified Bootloader version 2. Once the BIOS locates the grub2 bootloader, it executes and loads it onto the main memory (RAM).
/boot/grub/grub.cfg -
Kernel Stage
the kernel that was selected by GRUB first mounts the root file system that’s specified in the grub.conf file. Then it executes the /sbin/init program, which is always the first program to be executed. You can confirm this with its process id (PID), which should always be 1.
Init is always the first program to be executed and is assigned the process ID or PID of 1. It’s the init process that spawns various daemons & mounts all partitions that are specified in the /etc/fstab file.
The kernel then mounts the initial RAM disk (initrd) which is a temporary root filesystem until the real root filesystem is mounted. All kernels are located in the /boot directory together with the initial RAM disk image. -
systemd
Systemd process is located in /lib/system/systemd.
Systemd then loads the rest of the scripts to make the operating system fully functional for the user. These scripts are called units located under directory /lib/systemd/system.
Systemd uses the /etc/systemd/system/default.target file to determine the state or target that the Linux system should boot into.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Kernel
-
kernel
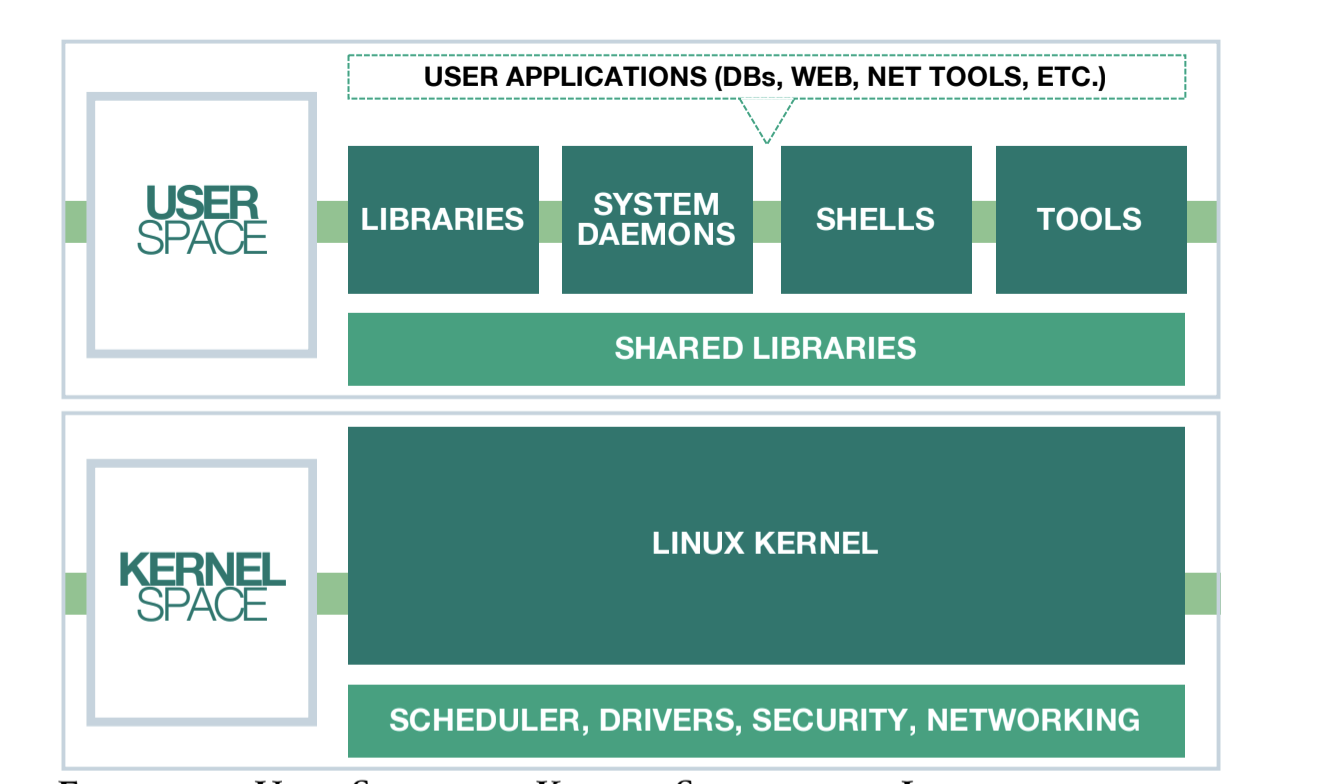
The kernel is the special piece of the operating system that controls the CPU hardware, allocates memory, accesses data, schedules processes, runs the applications, and protects them from each other. It is the first program loaded on the computer when the computer starts up. The most critical pieces of code in the kernel are loaded into protected areas of memory so that they can’t be overwritten by other applications running in the operating system. -
distribution
“distro,” a Linux distribution is the combination of specific versions of the Linux kernel with other libraries, system daemons, development tools, applications, packaging, and life-cycle management tools that are compatible with each other and tested for interoperability. -
kernel space
Operating systems all execute their kernel in protected and restricted memory that is called kernel space to prevent the kernel from terminating and crashing the system.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
refer