Openstack
OpenStack is a cloud operating system that controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources throughout a datacenter, all managed through a dashboard that gives administrators control while empowering their users to provision resources through a web interface.
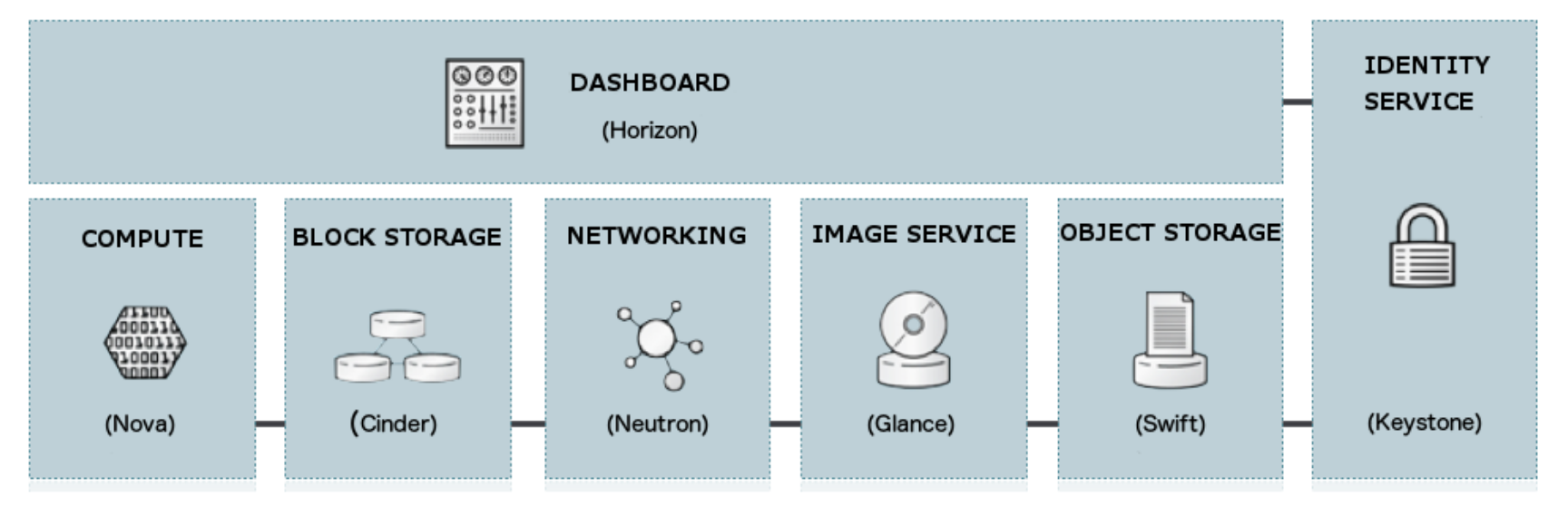
Openstack Component
 (°0°)
(°0°)
Compute (Nova)
OpenStack Compute is a cloud computing fabric controller, which manages pools of computer resources and work with virtualization technologies, bare metals, and high-performance computing configurations. Nova’s architecture provides flexibility to design the cloud with no proprietary software or hardware requirements and also delivers the ability to integrate the legacy systems and third-party products.
Nova can be deployed using hypervisor technologies such as KVM, VMware, LXC, XenServer, etc. It is used to manage numerous virtual machines and other instances that handle various computing tasks.
Image Service (Glance)
OpenStack image service offers discovering, registering, and restoring virtual machine images. Glance has client-server architecture and delivers a user REST API, which allows querying of virtual machine image metadata and also retrieval of the actual image. While deploying new virtual machine instances, Glance uses the stored images as templates.
OpenStack Glance supports Raw, VirtualBox (VDI), VMWare (VMDK, OVF), Hyper-V (VHD), and Qemu/KVM (qcow2) virtual machine images.
Object Storage (Swift)
OpenStack Swift creates redundant, scalable data storage to store petabytes of accessible data. The stored data can be leveraged, retrieved and updated. It has a distributed architecture, providing greater redundancy, scalability, and performance, with no central point of control.
Swift is a profoundly available, shared, eventually consistent object store. It helps organizations to store lots of data safely, cheaply and efficiently. Swift ensures data replication and distribution over various devices, which makes it ideal for cost-effective, scale-out storage.
Dashboard (Horizon)
Horizon is the authorized implementation of OpenStack’s Dashboard, which is the only graphical interface to automate cloud-based resources. To service providers and other commercial vendors, it supports with third party services such as monitoring, billing, and other management tools. Developers can automate tools to manage OpenStack resources using EC2 compatibility API or the native OpenStack API.
Identity Service (Keystone)
Keystone provides a central list of users, mapped against all the OpenStack services, which they can access. It integrates with existing backend services such as LDAP while acting as a common authentication system across the cloud computing system.
Keystone supports various forms of authentication like standard username & password credentials, AWS-style (Amazon Web Services) logins and token-based systems. Additionally, the catalog provides an endpoint registry with a queryable list of the services deployed in an OpenStack cloud.
Networking (Neutron)
Neutron provides networking capability like managing networks and IP addresses for OpenStack. It ensures that the network is not a limiting factor in a cloud deployment and offers users with self-service ability over network configurations. OpenStack networking allows users to create their own networks and connect devices and servers to one or more networks. Developers can use SDN technology to support great levels of multi-tenancy and massive scale.
Neutron also offers an extension framework, which supports deploying and managing of other network services such as virtual private networks (VPN), firewalls, load balancing, and intrusion detection system (IDS)
Block Storage (Cinder)
OpenStack Cinder delivers determined block-level storage devices for application with OpenStack compute instances. A cloud user can manage their storage needs by integrating block storage volumes with Dashboard and Nova.
Cinder can use storage platforms such as Linux server, EMC (ScaleIO, VMAX, and VNX), Ceph, Coraid, CloudByte, IBM, Hitachi data systems, SAN volume controller, etc. It is appropriate for expandable file systems and database storage.
Telemetry (Ceilometer)
Ceilometer delivers a single point of contact for billing systems obtaining all of the measurements to authorize customer billing across all OpenStack core components. By monitoring notifications from existing services, developers can collect the data and may configure the type of data to meet their operating requirements.
Orchestration (Heat)
Heat is a service to orchestrate multiple composite cloud applications through both the CloudFormation-compatible Query API and OpenStack-native REST API, using the AWS CloudFormation template format.
Openstack vs k8s
Openstack: infrastructure as a service
k8s: platform as a service
Openstack vs AWS
refer