RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is messaging software built on the AMQP protocol. Applications and services can exchange messages via queues managed by a RabbitMQ broker.
Messages are not published directly to a queue, instead, the producer sends messages to an exchange.
 (°0°)
(°0°)
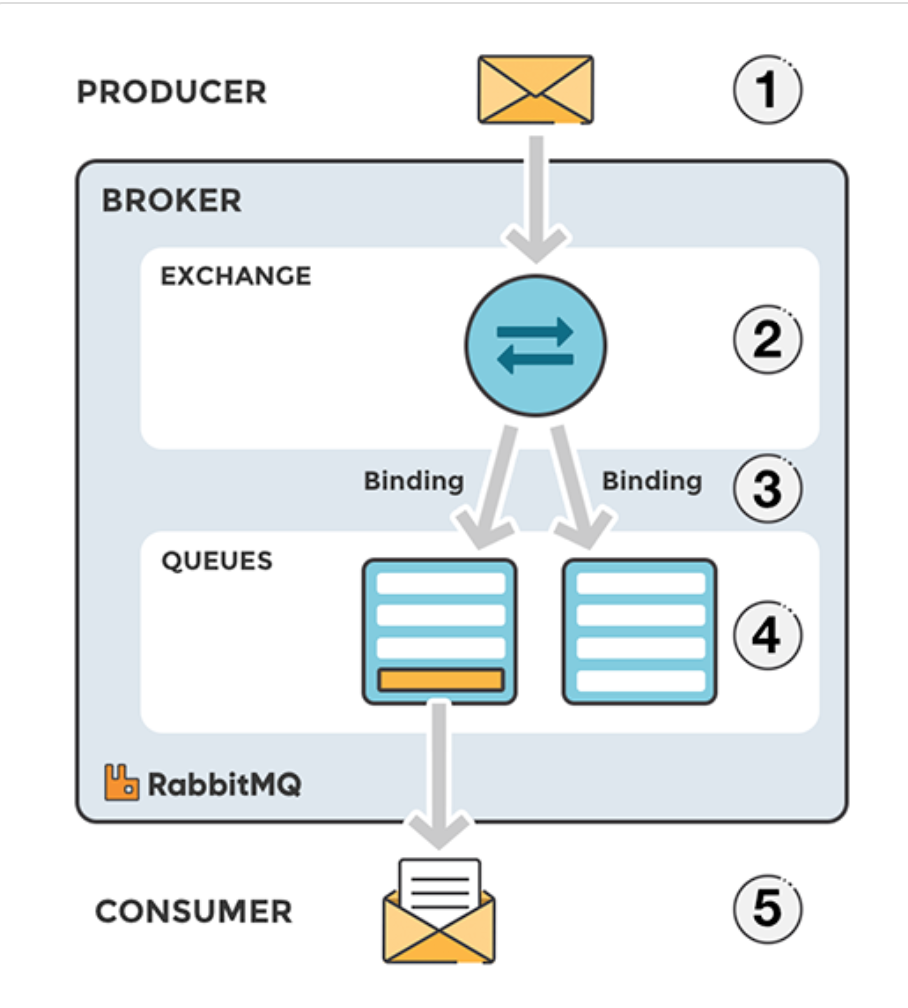
Message flow in RabbitMQ:
1,The producer publishes a message to an exchange. When you create the exchange, you have to specify the type of it. The different types of exchanges are explained in detail later on.
2,The exchange receives the message and is now responsible for the routing of the message. The exchange takes different message attributes into account, such as routing key, depending on the exchange type.
3,Bindings have to be created from the exchange to queues. In this case, we see two bindings to two different queues from the exchange. The Exchange routes the message into the queues depending on message attributes.
4,The messages stay in the queue until they are handled by a consumer
5,The consumer handles the message.
shovel
Shovel is a plugin for RabbitMQ that enables you to define replication relationships between brokers. It can for example be used to balance the load of a queue or when you need to be able to take messages out of one RabbitMQ broker, and insert them into another.
Imagen that you have a CloudAMQP instance with very high load on queue A. In that case you can create a shovel and configure it to consume the messages from queue A and republish them to an exchange in another CloudAMQP instance.
RabbitMQ vs Kafka
performance
push vs pull
AMQP some guarantee
refer