Overview
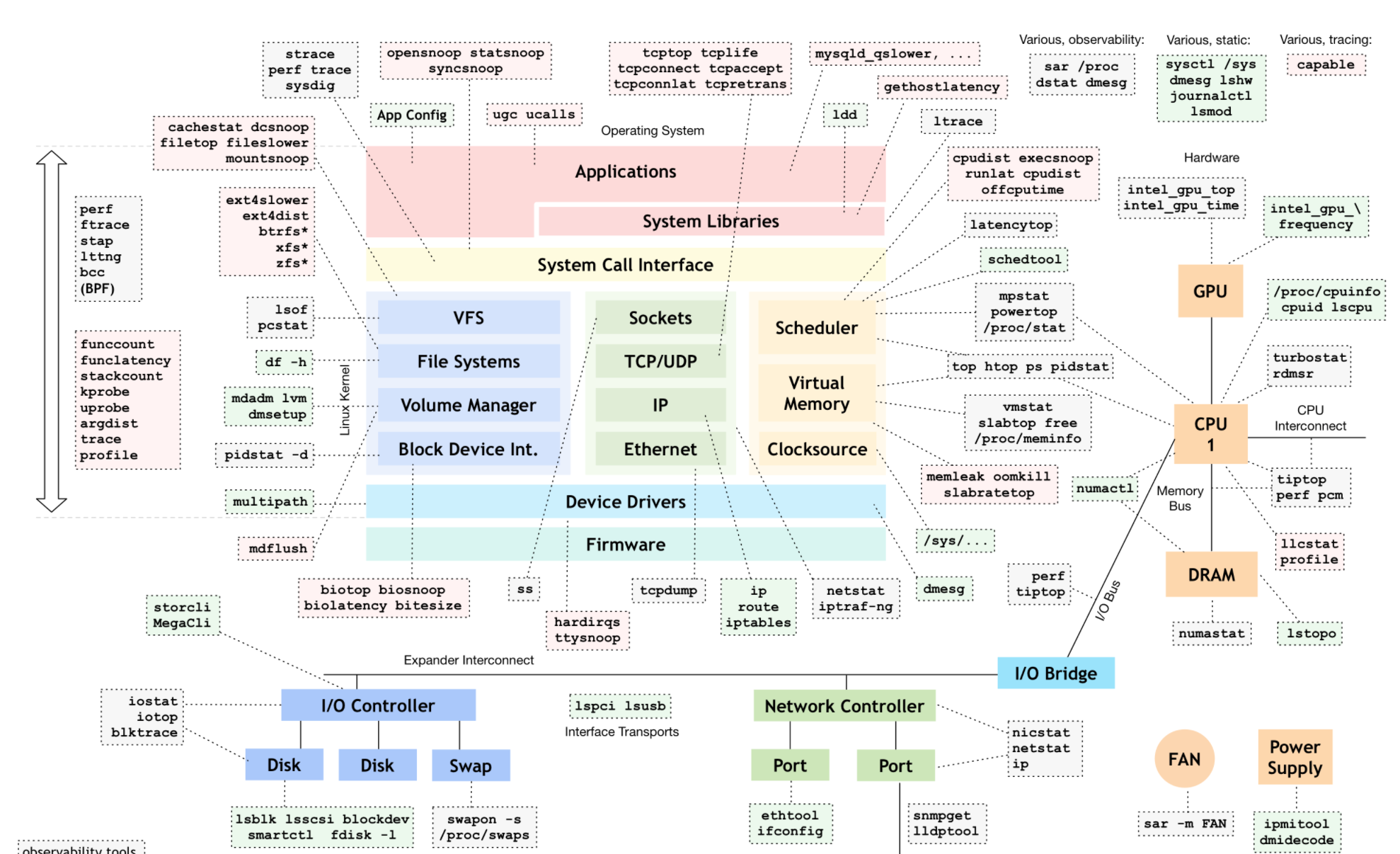 (°0°)
(°0°)
perf
refer
# perf record -F 99 -a -g -- sleep 60
# perf script > out.perf
Network
- port
nc -v host port - auto exit telnet
echo -e “^]\nclose”| telnet hostname 3306 -
tcpdump
- tcp state
netstat -an|awk ‘/^tcp/{++S[$NF]}END{for (a in S)print a,S[a]}’ -
nat
A(wan server):
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s source/24 -o em1 -j MASQUERADE
iptables -A FORWARD -s source/24 -o em1 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A FORWARD -d source/24 -m state –state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -i em1 -j ACCEPT
B(lan server):
route add default gw Aip em2 -
network limit(wondershaper and trickle)
wondershaper {interface} {down} {up} – limit network interface
the {down} and {up} are bandwidth in kilobits. So for example if you want to limit the bandwidth of interface eth1 to 256kbps uplink and 128kbps downlink,
wondershaper eth1 256 128
To clear the limit,
wondershaper clear eth1
trickle -u {up} -d {down} {program} – limit programe
Both {up} and {down} and bandwidth in KB/s. Now if you invoke it as,
trickle -u 8 -d 8 firefox - test open port(without telnet)
$ timeout 1 bash -c ‘cat < /dev/null > /dev/tcp/ipaddress/80’
$ echo $?
cat < /dev/tcp/ipaddress/22 -
mtr(ping and traceroute)
mtr ip_address or dns
The Loss% column shows the percentage of packet loss at each hop.
The Snt column counts the number of packets sent.
Last is the latency(ms) of the last packet sent, Avg is average latency of all packets, while Best and Wrst display the best (shortest) and worst (longest) round trip time for a packet to this host.
mtr -P 80 -i 0.5 -rwc 50 example.com –mtr in tcp mode to test ports or firewall -
dig
dig +short domain @dnserver -
netstat -p
netstat -s -
whois
whois -h whois.apple.com ip_address - link layer
sudo lldpcli show neighbors - opening port
nmap localhost nmap <ip>
Memory
- memory leak check
valgrind –leak-check=yes myprog arg1 arg2 - memory stats
cat /proc/meminfo
vmstat -s
Disk
-
create raid 10
mdadm –create /dev/md3 –run –level=10 –chunk=4 –raid-devices=4 /dev/sdf1 /dev/sdg1 /dev/sdh1 /dev/sdi1 -
MegaCli64
MegaCli64 -PdList -aAll -
hdparm(diagnosis and tuning of hard drives)
hdparm -I /dev/sda | more -
smartctl
sudo smartctl –all /dev/sda
CPU
- command command
top or cat /proc/cpuinfo
Software
- search rpm repo
yum whatprovides tshark
Process
-
process diagnosis:
strace -c -p pid -
process env
/proc/$(pidof kafka)/limits -
parent process
ps axfo pid,ppid,command -
pstree
File
- list open files
lsof:COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
FD – Represents the file descriptor. Some of the values of FDs are,
cwd – Current Working Directory
txt – Text file
mem – Memory mapped file
mmap – Memory mapped device
NUMBER – Represent the actual file descriptor. The character after the number i.e ‘1u’, represents the mode in which the file is opened. r for read, w for write, u for read and write.
TYPE – Specifies the type of the file. Some of the values of TYPEs are,
REG – Regular File
DIR – Directory
FIFO – First In First Out
CHR – Character special file
Hardware
-
hardware info:
dmidecode -
hardware digest:
demsg
Process
systemctl list-units
pstree
lsof
others
sed -i '' -e "s/string1/string2/g" file
curl
- view curl version
curl --version - save the cURL output to a file
curl -o result.html https://www.apple.com - fetch multiple files at a time
curl -O URL1 -O URL2 - follow HTTP location headers(redirect)
curl -L http://www.google.com - Continue/Resume a previous download
curl -C - -O http://www.google.com - limit the rate of data transfer
curl --limit-rate 1000B -O http://www.google.com - Download a file only if it is modified before/after the given time
curl -z 21-Dec-11 http://www.google.com - Pass HTTP authentication in cURL
curl -u username:password URL - Download Files from FTP server
curl -u ftpuser:ftppass -O ftp://ftp_server - List/Download using Ranges
curl ftp://ftp.com/main/[a-z]/ - Upload files to FTP server
curl -u ftpuser:ftppass -T local.txt ftp://ftp.server - More information using Verbose and Trace Option
curl -v -trace http://google.com/sg - Use proxy to download a file
curl -x proxyserver.test.com:2121 http://apple.com/sg - Download URLs from a file
xargs -n 1 curl -O < listurls.txt - Query HTTP Headers
curl -I www.apple.com - Make a Post request with Parameters
curl --data "firstName=aa&lastName=bb" https://login.com - Specify User Agent
curl -I http://www.google.comn --user-agent "I am a new web browser" - Store website cookies
curl --cookie-jar cnncookies.txt https://www.cnn.com -O curl --cookie cnncookies.txt https://www.cnn.com - Modify Name Resolution(tell curl to request the site from localhost instead of using DNS or /etc/hosts)
curl --resolve www.domain.com:80:localhost http://www.domain.com/ - curl with TLS client certificate
```
A. generate a client private key client.key and certificate signing request client.csr
openssl req -new -config “cnfile” -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout client.key -out client.csr
B. submit the certificate signing request client.csr to a CA and get back a CA-signed certificate(CA will sign out client cert signing request using their CA-cert and CA +++private key, and give us back a signed client certificate client.crt)
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -out client.crt -CA server.crt -CAkey server.key -set_serial 01 -days 365
C. curl with client.crt and client.key
curl –request POST \
–url https://example.com/hello \
–cert client.crt \
–key client.key \
–header ‘Content-Type: application/json’ \
–verbose \
-d @- \
« EOF
{
“hello”: “world”
}
EOF
curl -X POST -H “Content-Type: application/json” -H “xxx” -d ‘json content’
20. check HTTP status code
curl -s –write-out ‘%{http_code}’ http://kushaldas.in -o /dev/null
21. Doing multiple requests at once
curl –user-agent “ABC/1.0” http://a.com –next https://b.com
22. curl with key, cert and token
curl -vk –key private-client-key.pem –cert xx.com.chain.pem -H ‘Accept: application/json’ -H “Authorization: Bearer $(cat token-api)” “https://www”2
** openssl **
1. checking certificate validity
echo | openssl s_client -connect redhat.com:443 -brief
2. determing when a certificate expires
echo | openssl s_client -connect redhat.com:443 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout dates
3. checking certificate extensions
X509 extensions allow for additional fields to be added to a certificate. One of the most common is the subject alternative name(SAN). The SAN of a certificate allows multiple values +++to be assoicated with a single cert.
echo | openssl s_client -connect redhat.com:443 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -ext subjectAltName
4. checking deprecated TLS ciphers or versions
openssl ciphers -s tls1_3
5. Inspecting a certificate
openssl x509 -text -noout -in /usr/share/ca-certificates/mozilla/VeriSign_Universal_Root_Certification_Authority.crt
6. geenrating some random data
openssl rand -base64 9
cat /dev/urandom | head -c 50 | openssl base64 | openssl base64 -d # Base64 encoding and decoding
7. Generate an RSA key
openssl genrsa -out example.key [bits]
8. Create X.509 certificates
openssl req -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout example.key -out example.crt -x509 -days 365
openssl x509 -req -in example.csr -signkey example.key -out example.crt -days 365 #using existing CSR and private key
openssl x509 -in example.crt -text -noout # print textual representation of the cert
openssl x509 -in cert.pem -fingerprint -sha256 -noout # Print certificate’s fingerprint as md5, sha1, sha256 digest
9. verify CSRs or cert
openssl req -in example.csr -verify
openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in example.key | openssl sha256
openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in example.crt | openssl sha256
openssl req -noout -modulus -in example.csr | openssl sha256
10. TLS client to connect to a remote server
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443
11. Convert between encoding and container formats
Convert certificate between DER and PEM formats:
openssl x509 -in example.pem -outform der -out example.der
openssl x509 -in example.der -inform der -out example.pem
```
- pgp, public key
wget -qO - https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | gpg -v
wget -qO https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg.asc > google-cloud.key
gpg –keyring /tmp/temp.gpg –no-default-keyring –import google.gp
gpg –keyring /tmp/temp.gpg –no-default-keyring –export -a