 (°0°)
(°0°)
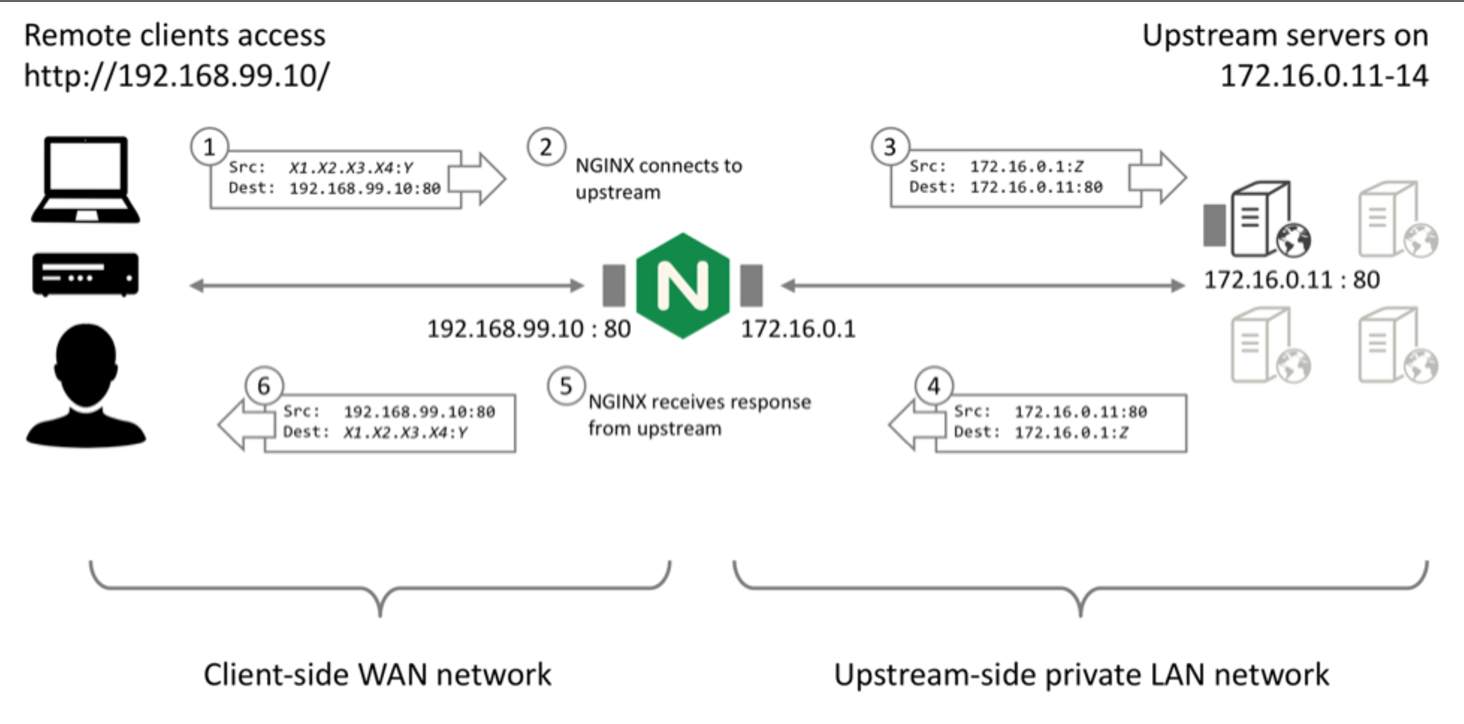 (°0°)
(°0°)
epoll,poll,select
Nginx supports the following connection method (I/O multiplexing method), these methods can be specified through the use command.
* select – The standard method. If the current platform is no more effective method, it is the compiler default. You can use configuration parameters - with-select_module and - without-select_module to enable or disable this module.
* poll – The standard method. If the current platform is no more effective method, it is the compiler default. You can use configuration parameters - with-poll_module and - without-poll_module to enable or disable this module.
* kqueue – Efficient method, used in FreeBSD 4.1+, OpenBSD 2.9+, MacOS NetBSD 2 and MacOS X. X system using dual processor using kqueue may cause kernel crash.
* epoll – Efficient method, system used in the Linux kernel version 2.6 and later. In some distributions, such as SuSE 8.2, there are 2.4 versions of epoll support in the kernel patch.
* rtsig – Real time signal can be performed using in the system, Linux kernel version 2.2.19 later. Not by default in the whole system more than 1024 real time POSIX (queuing) signal. This is inefficient for highly loaded servers; it is necessary to adjust the kernel parameter /proc/sys/kernel/rtsig-max to increase the queue size.
nginx worker,fastcgi,socket
LINUX Tuning For NGINX
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets=260000 —The maximum number of sockets in TIME_WAIT state allowed in the system.
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 —depend on “echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_timestamps”
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0 —Dangerous:reuse not clean tcp connection
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 10 —This specifies how many seconds to wait for a final FIN packet before the socket is forcibly closed.
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 10000 65000 —more ports can be used
net.core.somaxconn = 65535
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 65535
sys.fs.file_max = 3252969
nofile = 655350
for tcp keepalive:
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 900 –try to send detect package after no data
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 30 – interval between two detect
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3 –detect times
so_keepalive=on|off|[keepidle]:[keepintvl]:[keepcnt]
for http keep-alive:
keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout] –
keepalive_requests –
Nginx Configuration Tuning
worker_processes – more than 1/2 cpu cores
worker_cpu_affinity
worker_connections
client_body_buffer_size 10K;
client_header_buffer_size 1k;
client_max_body_size 8m;
large_client_header_buffers 2 1k;
client_body_timeout 12;
client_header_timeout 12;
keepalive_timeout 15;
send_timeout 10;
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_min_length 1000;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/xml text/css application/xml;
location ~* .(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js)$ {
expires 365d;
}
access_log off;
keepalive
HTTP Keep-Alive is a feature that allows HTTP client (usually browser) and server (webserver) to send multiple request/response pairs over the same TCP connection. This decreases latency for 2nd, 3rd,… HTTP request, decreases network traffic and similar.
TCP keepalive is a totally different beast. It keeps TCP connection opened by sending small packets. Additionally, when the packet is sent this serves as a check so the sender is notified as soon as connection drops (note that this is NOT the case otherwise - until we try to communicate through TCP connection we have no idea if it is ok or not).
for tcp keepalive:
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 900 –try to send detect package after no data
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 30 – interval between two detect
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3 –detect times
so_keepalive=on|off|[keepidle]:[keepintvl]:[keepcnt]
keepalive –upstream
proxy_http_version 1.1
proxy_set_header Connection “”
for http keep-alive:
keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout]
keepalive_requests
HTTP(S) Web Server
static:
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.samuel.com;
location / {
root /var/www/test.samuel.com;
index index.html;
}
}
}dynamic:
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.samuel.com;
location / {
fastcgi_pass localhost:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /home/www/scripts/php\$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING \$query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD \$request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE \$content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH \$content_length;
}
}
}http forward proxy:
server {
listen 80;
server_name kafka_offset_monitor.com;
charset utf-8;
location /kafka_1/ {
proxy_pass http://ip1:8089/;
}
location /kafka_2/ {
proxy_pass http://ip2:8083/;
}
}https:
http {
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.samuel.com;
keepalive_timeout 70;
ssl_certificate www.samuel.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key www.samuel.com.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
server_name test.samuel.com;
location / {
root /var/www/test.samuel.com;
index index.html;
}
}
}TCP PROXY SERVER
tcp:
upstream db-mysql1 {
server ip:3306 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=60 weight=1;
server ip:3306 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=60 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 50001;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
proxy_timeout 1m;
proxy_pass db-mysql1;
allow ip1;
}